Euklidovský algoritmus je spôsob, ako nájsť najväčšieho spoločného deliteľa dvoch kladných celých čísel. GCD dvoch čísel je najväčšie číslo, ktoré ich delí. Jednoduchý spôsob, ako nájsť GCD, je faktorizovať čísla a vynásobiť spoločné prvočísla.
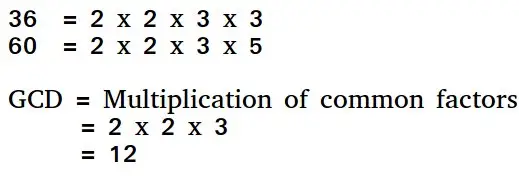
Základný euklidovský algoritmus pre GCD:
Algoritmus je založený na nižšie uvedených skutočnostiach.
- Ak odčítame menšie číslo od väčšieho (väčšie číslo znížime), GCD sa nezmení. Ak teda neustále odčítavame väčšie z dvoch, skončíme s GCD.
- Ak teraz namiesto odčítania vydelíme menšie číslo, algoritmus sa zastaví, keď nájdeme zvyšok 0.
Nižšie je uvedená rekurzívna funkcia na vyhodnotenie gcd pomocou Euklidovho algoritmu:
C
// C program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> #include> // Function to return gcd of a and b> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >if> (a == 0)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >int> a = 10, b = 15;> > >// Function call> >printf>(>'GCD(%d, %d) = %d
'>, a, b, gcd(a, b));> >a = 35, b = 10;> >printf>(>'GCD(%d, %d) = %d
'>, a, b, gcd(a, b));> >a = 31, b = 2;> >printf>(>'GCD(%d, %d) = %d
'>, a, b, gcd(a, b));> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
CPP
// C++ program to demonstrate> // Basic Euclidean Algorithm> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Function to return> // gcd of a and b> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >if> (a == 0)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> }> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >int> a = 10, b = 15;> > >// Function call> >cout <<>'GCD('> << a <<>', '> << b <<>') = '> << gcd(a, b)> ><< endl;> >a = 35, b = 10;> >cout <<>'GCD('> << a <<>', '> << b <<>') = '> << gcd(a, b)> ><< endl;> >a = 31, b = 2;> >cout <<>'GCD('> << a <<>', '> << b <<>') = '> << gcd(a, b)> ><< endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
bash čítaný súbor
>
Java
// Java program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> import> java.lang.*;> import> java.util.*;> class> GFG {> >// extended Euclidean Algorithm> >public> static> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >if> (a ==>0>)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> >}> >// Driver code> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >int> a =>10>, b =>15>, g;> > >// Function call> >g = gcd(a, b);> >System.out.println(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a =>35>;> >b =>10>;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >System.out.println(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a =>31>;> >b =>2>;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >System.out.println(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >}> }> // Code Contributed by Mohit Gupta_OMG> |
>
>
Python3
# Python3 program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> # Function to return gcd of a and b> def> gcd(a, b):> >if> a>=>=> 0>:> >return> b> >return> gcd(b>%> a, a)> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >a>=> 10> >b>=> 15> >print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, gcd(a, b))> >a>=> 35> >b>=> 10> >print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, gcd(a, b))> >a>=> 31> >b>=> 2> >print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, gcd(a, b))> # Code Contributed By Mohit Gupta_OMG> |
>
>
C#
// C# program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> using> System;> class> GFG {> >public> static> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >if> (a == 0)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> >}> >// Driver Code> >static> public> void> Main()> >{> >int> a = 10, b = 15, g;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >Console.WriteLine(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a = 35;> >b = 10;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >Console.WriteLine(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a = 31;> >b = 2;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >Console.WriteLine(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >}> }> // This code is contributed by ajit> |
>
>
PHP
// php program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> // PHP program to demonstrate // Basic Euclidean Algorithm // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // Driver Code $a = 10; $b = 15; // Function call echo 'GCD(',$a,',' , $b,') = ', gcd($a, $b); echo '
'; $a = 35; $b = 10; echo 'GCD(',$a ,',',$b,') = ', gcd($a, $b); echo '
'; $a = 31; $b = 2; echo 'GCD(',$a ,',', $b,') = ', gcd($a, $b); // This code is contributed by m_kit ?>> |
>
>
Javascript
// JavaScript program to demonstrate> // Basic Euclidean Algorithm> // Function to return> // gcd of a and b> function> gcd( a, b)> {> >if> (a == 0)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> }> // Driver Code> >let a = 10, b = 15;> >document.write(>'GCD('> + a +>', '> >+ b +>') = '> + gcd(a, b) +>' '>);> > >a = 35, b = 10;> >document.write(>'GCD('> + a +>', '> >+ b +>') = '> + gcd(a, b) +>' '>);> > >a = 31, b = 2;> >document.write(>'GCD('> + a +>', '> >+ b +>') = '> + gcd(a, b) +>' '>);> // This code contributed by aashish1995> |
>
>Výkon
GCD(10, 15) = 5 GCD(35, 10) = 5 GCD(31, 2) = 1>
Časová zložitosť: O (Log min(a, b))
Pomocný priestor: O(Log (min(a,b))
Rozšírený euklidovský algoritmus:
Rozšírený euklidovský algoritmus tiež nájde celočíselné koeficienty x a y také, že: ax + by = gcd(a, b)
Príklady:
Vstup: a = 30, b = 20
Výkon: gcd = 10, x = 1, y = -1
(Upozorňujeme, že 30*1 + 20*(-1) = 10)Vstup: a = 35, b = 15
Výkon: gcd = 5, x = 1, y = -2
(Upozorňujeme, že 35*1 + 15*(-2) = 5)
Rozšírený euklidovský algoritmus aktualizuje výsledky gcd(a, b) pomocou výsledkov vypočítaných rekurzívnym volaním gcd(b%a, a). Nech hodnoty x a y vypočítané rekurzívnym volaním sú x1a y1. x a y sa aktualizujú pomocou nižšie uvedených výrazov.
Odporúčaná prax Rozšírený euklidovský algoritmus Vyskúšajte to!ax + by = gcd(a, b)
gcd(a, b) = gcd(b%a, a)
gcd(b%a, a) = (b%a)x1+ je1
ax + by = (b%a)x1+ je1
ax + by = (b – [b/a] * a)x1+ je1
ax + by = a(y1– [b/a] * x1) + bx1Porovnanie LHS a RHS,
x = y1– ?b/a? * X1
y = x1
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia vyššie uvedeného prístupu:
C++
markíza html
// C++ program to demonstrate working of> // extended Euclidean Algorithm> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Function for extended Euclidean Algorithm> int> gcdExtended(>int> a,>int> b,>int> *x,>int> *y)> {> >// Base Case> >if> (a == 0)> >{> >*x = 0;> >*y = 1;> >return> b;> >}> >int> x1, y1;>// To store results of recursive call> >int> gcd = gcdExtended(b%a, a, &x1, &y1);> >// Update x and y using results of> >// recursive call> >*x = y1 - (b/a) * x1;> >*y = x1;> >return> gcd;> }> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >int> x, y, a = 35, b = 15;> >int> g = gcdExtended(a, b, &x, &y);> >cout <<>'GCD('> << a <<>', '> << b> ><<>') = '> << g << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
C
// C program to demonstrate working of extended> // Euclidean Algorithm> #include> // C function for extended Euclidean Algorithm> int> gcdExtended(>int> a,>int> b,>int> *x,>int> *y)> {> >// Base Case> >if> (a == 0)> >{> >*x = 0;> >*y = 1;> >return> b;> >}> >int> x1, y1;>// To store results of recursive call> >int> gcd = gcdExtended(b%a, a, &x1, &y1);> >// Update x and y using results of recursive> >// call> >*x = y1 - (b/a) * x1;> >*y = x1;> >return> gcd;> }> // Driver Program> int> main()> {> >int> x, y;> >int> a = 35, b = 15;> >int> g = gcdExtended(a, b, &x, &y);> >printf>(>'gcd(%d, %d) = %d'>, a, b, g);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java program to demonstrate working of extended> // Euclidean Algorithm> import> java.lang.*;> import> java.util.*;> class> GFG {> >// extended Euclidean Algorithm> >public> static> int> gcdExtended(>int> a,>int> b,>int> x,> >int> y)> >{> >// Base Case> >if> (a ==>0>) {> >x =>0>;> >y =>1>;> >return> b;> >}> >int> x1 =>1>,> >y1 =>1>;>// To store results of recursive call> >int> gcd = gcdExtended(b % a, a, x1, y1);> >// Update x and y using results of recursive> >// call> >x = y1 - (b / a) * x1;> >y = x1;> >return> gcd;> >}> >// Driver Program> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >int> x =>1>, y =>1>;> >int> a =>35>, b =>15>;> >int> g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y);> >System.out.print(>'gcd('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate working of extended> # Euclidean Algorithm> # function for extended Euclidean Algorithm> def> gcdExtended(a, b):> ># Base Case> >if> a>=>=> 0>:> >return> b,>0>,>1> >gcd, x1, y1>=> gcdExtended(b>%> a, a)> ># Update x and y using results of recursive> ># call> >x>=> y1>-> (b>/>/>a)>*> x1> >y>=> x1> >return> gcd, x, y> # Driver code> a, b>=> 35>,>15> g, x, y>=> gcdExtended(a, b)> print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, g)> |
>
>
C#
// C# program to demonstrate working> // of extended Euclidean Algorithm> using> System;> class> GFG> {> > >// extended Euclidean Algorithm> >public> static> int> gcdExtended(>int> a,>int> b,> >int> x,>int> y)> >{> >// Base Case> >if> (a == 0)> >{> >x = 0;> >y = 1;> >return> b;> >}> >// To store results of> >// recursive call> >int> x1 = 1, y1 = 1;> >int> gcd = gcdExtended(b % a, a, x1, y1);> >// Update x and y using> >// results of recursive call> >x = y1 - (b / a) * x1;> >y = x1;> >return> gcd;> >}> > >// Driver Code> >static> public> void> Main ()> >{> >int> x = 1, y = 1;> >int> a = 35, b = 15;> >int> g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y);> >Console.WriteLine(>'gcd('> + a +>' , '> +> >b +>') = '> + g);> >}> }> |
>
>
PHP
// PHP program to demonstrate // working of extended // Euclidean Algorithm // PHP function for // extended Euclidean // Algorithm function gcdExtended($a, $b, $x, $y) { // Base Case if ($a == 0) { $x = 0; $y = 1; return $b; } // To store results // of recursive call $gcd = gcdExtended($b % $a, $a, $x, $y); // Update x and y using // results of recursive // call $x = $y - floor($b / $a) * $x; $y = $x; return $gcd; } // Driver Code $x = 0; $y = 0; $a = 35; $b = 15; $g = gcdExtended($a, $b, $x, $y); echo 'gcd(',$a; echo ', ' , $b, ')'; echo ' = ' , $g; ?>> |
>
>
Javascript
> // Javascript program to demonstrate> // working of extended> // Euclidean Algorithm> // Javascript function for> // extended Euclidean> // Algorithm> function> gcdExtended(a, b,> >x, y)> {> >// Base Case> >if> (a == 0)> >{> >x = 0;> >y = 1;> >return> b;> >}> >// To store results> >// of recursive call> >let gcd = gcdExtended(b % a,> >a, x, y);> >// Update x and y using> >// results of recursive> >// call> >x = y - (b / a) * x;> >y = x;> >return> gcd;> }> // Driver Code> let x = 0;> let y = 0;> let a = 35;> let b = 15;> let g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y);> document.write(>'gcd('> + a);> document.write(>', '> + b +>')'>);> document.write(>' = '> + g);> > |
>
>
Výkon :
gcd(35, 15) = 5>
Časová zložitosť: O (log N)
Pomocný priestor: O (log N)
Ako funguje rozšírený algoritmus?
Ako je vidieť vyššie, x a y sú výsledky pre vstupy a a b,
a.x + b.y = gcd —-(1)
A x1a y1sú výsledky pre vstupy b%a a a
(b%a).x1+ a.y1= gcd
Keď vyššie vložíme b%a = (b – (?b/a?).a),
sledujeme. Všimnite si, že ?b/a? je podlaha (b/a)(b – (?b/a?).a).x1+ a.y1= gcd
Vyššie uvedená rovnica môže byť tiež napísaná nižšie
b.x1+ a.(a1– (?b/a?).x1) = gcd — (2)
nohy vs nohaPo porovnaní koeficientov „a“ a „b“ v (1) a
(2), sledujeme,
x = y1– ?b/a? * X1
y = x1
Ako je užitočný rozšírený algoritmus?
Rozšírený euklidovský algoritmus je obzvlášť užitočný, keď a a b sú koprimé (alebo gcd je 1). Pretože x je modulárna multiplikatívna inverzia k a modulo b a y je modulárna multiplikatívna inverzia k b modulo a. Najmä výpočet modulárnej multiplikatívnej inverznej metódy je základným krokom v metóde šifrovania RSA verejným kľúčom.
