 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Algoritmus spätného vymazania úzko súvisí s Kruskalov algoritmus . V Kruskalovom algoritme robíme: Triedenie hrán podľa zvyšovania poradia ich váh. Po triedení postupne vyberáme hrany v rastúcom poradí. Aktuálnu vybratú hranu zahrnieme, ak jej zahrnutím do kostry nevytvorí žiadny cyklus, kým v kostre nie sú hrany V-1, kde V = počet vrcholov.
V algoritme Reverse Delete triedime všetky hrany klesajúci poradie ich hmotnosti. Po triedení postupne vyberáme okraje v zostupnom poradí. my zahrnúť aktuálnu zvolenú hranu, ak vylúčenie prúdovej hrany spôsobí odpojenie v prúdovom grafe . Hlavnou myšlienkou je vymazať hranu, ak jej vymazanie nevedie k odpojeniu grafu.
rozhranie v jazyku Java
Algoritmus:
- Zoraďte všetky hrany grafu v nezvyšujúcom sa poradí podľa váh hrán.
- Inicializujte MST ako pôvodný graf a odstráňte extra hrany pomocou kroku 3.
- Vyberte hranu s najvyššou hmotnosťou zo zostávajúcich hrán a skontrolujte, či odstránením hrany dôjde k odpojeniu grafu alebo nie .
Ak sa odpojí, okraj nevymažeme.
V opačnom prípade odstránime okraj a pokračujeme.
Ilustrácia:
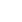
Pochopme to na nasledujúcom príklade:
Ak vymažeme najvyššiu hranu hmotnosti grafu 14, graf sa nerozpojí, tak ho odstránime.
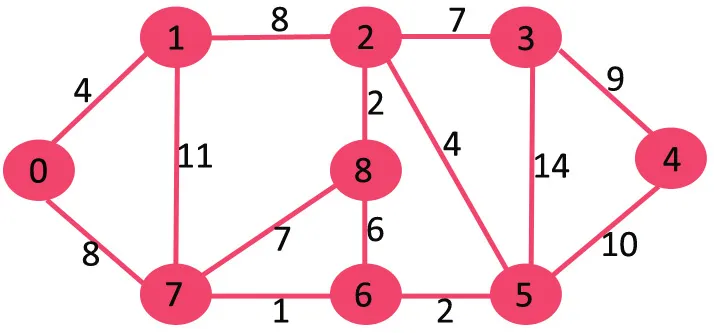
Ďalej vymažeme 11, pretože jeho odstránením sa graf neodpojí.
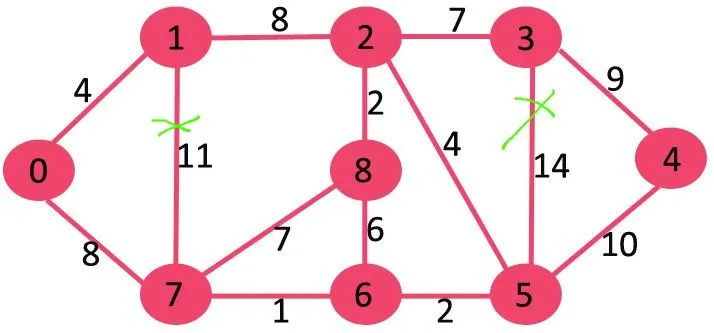
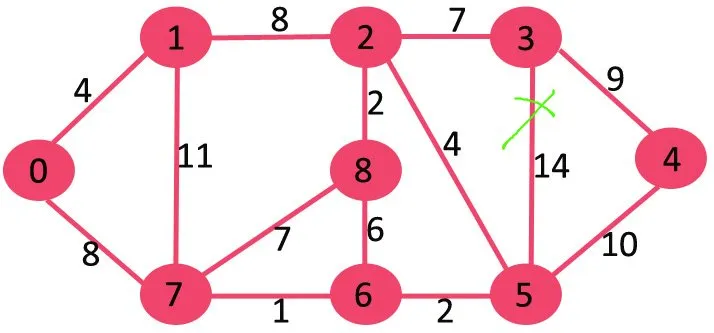
Ďalej vymažeme 10, pretože jej odstránením sa graf neodpojí.

Ďalej je 9. Nemôžeme odstrániť 9, pretože jej odstránenie spôsobí odpojenie.

Takto pokračujeme a nasledujúce hrany zostanú vo finálnom MST.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
Poznámka: V prípade okrajov rovnakej hmotnosti môžeme vybrať ľubovoľnú hranu s rovnakou hmotnosťou.
vlc stiahnite si videá z youtubeOdporúčaná prax Obrátený algoritmus vymazania pre minimálny Spanning Tree Skúste to!
Implementácia:
C++// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #include
// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.*; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { int u v w; Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.w = w; this.v = v; } public int compareTo(Edge other) { return (this.w - other.w); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<Integer>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; @SuppressWarnings({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new ArrayList[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>(); edges = new ArrayList<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v boolean[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for (int i : adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected() { boolean[] visited = new boolean[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections.sort(edges); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST System.out.println('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges.get(i).u; int v = edges.get(i).v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].remove(adj[u].indexOf(v)); adj[v].remove(adj[v].indexOf(u)); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].add(v); adj[v].add(u); // This edge is part of MST System.out.println('(' + u + ' ' + v + ')'); mst_wt += edges.get(i).w; } } System.out.println('Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; GFG g = new GFG(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_Dey
# Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__(self v): # No. of vertices self.v = v self.adj = [0] * v self.edges = [] for i in range(v): self.adj[i] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self u: int v: int w: int): self.adj[u].append(v) # Add w to v’s list. self.adj[v].append(u) # Add w to v’s list. self.edges.append((w (u v))) def dfs(self v: int visited: list): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self.adj[v]: if not visited[i]: self.dfs(i visited) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected(self): visited = [False] * self.v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self.dfs(0 visited) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range(1 self.v): if not visited[i]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST(self): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self.edges.sort(key = lambda a: a[0]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print('Edges in MST') # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range(len(self.edges) - 1 -1 -1): u = self.edges[i][1][0] v = self.edges[i][1][1] # Remove edge from undirected graph self.adj[u].remove(v) self.adj[v].remove(u) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self.connected() == False: self.adj[u].append(v) self.adj[v].append(u) # This edge is part of MST print('( %d %d )' % (u v)) mst_wt += self.edges[i][0] print('Total weight of MST is' mst_wt) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph(V) # making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4) g.addEdge(0 7 8) g.addEdge(1 2 8) g.addEdge(1 7 11) g.addEdge(2 3 7) g.addEdge(2 8 2) g.addEdge(2 5 4) g.addEdge(3 4 9) g.addEdge(3 5 14) g.addEdge(4 5 10) g.addEdge(5 6 2) g.addEdge(6 7 1) g.addEdge(6 8 6) g.addEdge(7 8 7) g.reverseDeleteMST() # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552
// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable<Edge> { public int u v w; public Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.v = v; this.w = w; } public int CompareTo(Edge other) { return this.w.CompareTo(other.w); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<int>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; public Graph(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new List<int>[ v ]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new List<int>(); edges = new List<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].Add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].Add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.Add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v bool[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach(int i in adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected() { bool[] visited = new bool[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges.Sort(); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST Console.WriteLine('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges[i].u; int v = edges[i].v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].Remove(v); adj[v].Remove(u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].Add(v); adj[v].Add(u); // This edge is part of MST Console.WriteLine('({0} {1})' u v); mst_wt += edges[i].w; } } Console.WriteLine('Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main(string[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; Graph g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
// Javascript program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { // Constructor constructor(V) { this.V = V; this.adj = []; this.edges = []; for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { this.adj[i] = []; } } // function to add an edge to graph addEdge(u v w) { this.adj[u].push(v);// Add w to v’s list. this.adj[v].push(u);// Add w to v’s list. this.edges.push([w [u v]]); } DFS(v visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; for (const i of this.adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) { this.DFS(i visited); } } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false isConnected() { const visited = []; for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { visited[i] = false; } // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex this.DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (let i = 1; i < this.V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { return false; } } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not reverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost this.edges.sort((a b) => a[0] - b[0]); let mstWt = 0;// Initialize weight of MST console.log('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (let i = this.edges.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { const [u v] = this.edges[i][1]; // Remove edge from undirected graph this.adj[u] = this.adj[u].filter(x => x !== v); this.adj[v] = this.adj[v].filter(x => x !== u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (!this.isConnected()) { this.adj[u].push(v); this.adj[v].push(u); // This edge is part of MST console.log(`(${u} ${v})`); mstWt += this.edges[i][0]; } } console.log(`Total weight of MST is ${mstWt}`); } } // Driver code function main() { // create the graph given in above figure var V = 9; var g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4); g.addEdge(0 7 8); g.addEdge(1 2 8); g.addEdge(1 7 11); g.addEdge(2 3 7); g.addEdge(2 8 2); g.addEdge(2 5 4); g.addEdge(3 4 9); g.addEdge(3 5 14); g.addEdge(4 5 10); g.addEdge(5 6 2); g.addEdge(6 7 1); g.addEdge(6 8 6); g.addEdge(7 8 7); g.reverseDeleteMST(); } main();
Výstup
Edges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37
Časová zložitosť: O((E*(V+E)) + E log E) kde E je počet hrán.
Priestorová zložitosť: O(V+E) kde V je počet vrcholov a E je počet hrán. Na uloženie grafu používame zoznam susedstiev, takže potrebujeme priestor úmerný O(V+E).
Poznámky:
- Vyššie uvedená implementácia je jednoduchou/naivnou implementáciou algoritmu Reverse Delete a možno ju optimalizovať na O(E log V (log log V)3) [Zdroj: Týždeň ]. Ale táto optimalizovaná časová zložitosť je stále menšia ako Prim a Kruskal Algoritmy pre MST.
- Vyššie uvedená implementácia modifikuje pôvodný graf. Ak je potrebné zachovať pôvodný graf, môžeme vytvoriť kópiu grafu.
Vytvoriť kvíz
