Vzhľadom na a spojený neorientovaný graf reprezentovaný zoznamom susedstva adjList[][] s n uzly a m hrany, pričom každý uzol má a zreteľné označenie od 0 až n-1 a každý adj[i] predstavuje zoznam vrcholov pripojených k vertexu i.
Vytvorte a klonovať grafu, kde každý uzol v grafe obsahuje celé číslo val a pole ( susedov ) uzlov obsahujúce uzly, ktoré susedia s aktuálnym uzlom.
class Node {
val: celé číslo
susedia: Zoznam[Uzol]
}pátranie protivníka
Vašou úlohou je naklonovať daný graf a vrátiť referenciu na naklonovaný graf.
Poznámka: Ak vrátite správnu kópiu daného grafu, výstup bude pravdivý; v opačnom prípade, ak je kópia nesprávna, vytlačí sa nesprávne.
Príklady
aktuálny dátum java
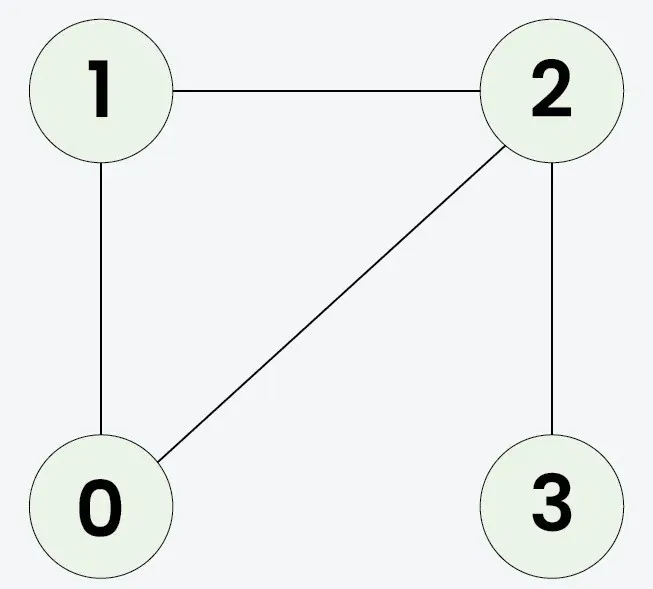
Vstup: n = 4 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0 2] [0 1 3] [2]]
výstup: pravda
Vysvetlenie:
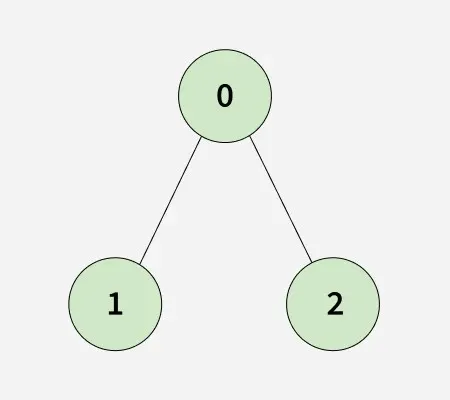
Keďže klonovaný graf je identický s originálom, výstup bude pravdivý.Vstup: n = 3 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0] [0]]
výstup: pravda
Vysvetlenie:
Keďže klonovaný graf je identický s originálom, výstup bude pravdivý.
Obsah
- Prečo potrebujeme sledovať navštívené/klonované uzly?
- Ako sledovať navštívené/klonované uzly?
- Ako pripojiť klonované uzly?
- Ako overiť, či je klonovaný graf správny?
- [Prístup 1] Použitie prechodu BFS – čas O(V+E) a priestor O(V)
- [Prístup 2] Použitie prechodu DFS – čas O(V+E) a priestor O(V)
Prečo potrebujeme sledovať navštívené/klonované uzly?
Musíme sledovať navštívené alebo klonované uzly, aby sme sa vyhli nekonečnej rekurzii a nadbytočnej práci pri klonovaní grafu. Keďže grafy môžu obsahovať cykly (kde môže uzol ukazovať späť na predtým navštívený uzol), bez sledovania uzlov, ktoré sme už naklonovali, funkcia klonovania by donekonečna prehodnocovala rovnaké uzly, čo by viedlo k pretečeniu zásobníka alebo nesprávnej duplikácii.
Ako sledovať navštívené/klonované uzly?
HashMap/Map je potrebná na zachovanie všetkých už vytvorených uzlov. Kľúčové sklady : Referencia/Adresa pôvodného uzla Hodnotné obchody : Referencia/Adresa klonovaného uzla Bola vytvorená kópia všetkých uzlov grafu.
Ako pripojiť klonované uzly?
Pri návšteve susedných vrcholov a uzol v získať zodpovedajúci klon uzol pre teba to nazvime IN teraz navštívte všetky susedné uzly v a pre každého suseda nájdite zodpovedajúci klonový uzol (ak sa nenájde, vytvorte ho) a potom ho zatlačte do susedného vektora IN uzol.
Ako overiť, či je klonovaný graf správny?
Vykonajte prechod BFS na pôvodnom grafe pred klonovaním a potom znova na klonovanom grafe po dokončení klonovania. Počas každého prechodu sa vytlačí hodnota každého uzla spolu s jeho adresou (alebo referenciou). Na overenie správnosti klonovania porovnajte poradie navštívených uzlov v oboch prechodoch. Ak sa hodnoty uzlov objavia v rovnakom poradí, ale ich adresy (alebo referencie) sa líšia, potvrdzuje to, že graf bol úspešne a správne naklonovaný.
Zistite, ako na to klonovanie neorientovaného grafu vrátane grafov s viacerými pripojenými komponentmi pomocou BFS alebo DFS na zabezpečenie úplnej hlbokej kópie všetkých uzlov a hrán.
[Prístup 1] Použitie prechodu BFS – čas O(V+E) a priestor O(V)
C++V prístupe BFS sa graf klonuje iteratívne pomocou frontu. Začneme klonovaním počiatočného uzla a umiestnením do frontu. Keď spracovávame každý uzol z frontu, navštevujeme jeho susedov. Ak sused ešte nebol klonovaný, vytvoríme klon, uložíme ho na mapu a zaradíme do frontu na neskoršie spracovanie. Potom pridáme klon suseda do zoznamu susedov aktuálneho klonu uzla. Tento proces pokračuje úroveň po úrovni, čím sa zabezpečí, že všetky uzly budú navštívené v poradí od šírky po prvé. BFS je obzvlášť užitočný na zabránenie hlbokej rekurzii a efektívne spracovanie veľkých alebo širokých grafov.
vrchný príkaz unix
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { public int val; public ArrayList<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; Map<Node Node> mp = new HashMap<>(); Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Clone the starting node Node clone = new Node(node.val); mp.put(node clone); q.offer(node); while (!q.isEmpty()) { Node current = q.poll(); for (Node neighbor : current.neighbors) { // Clone neighbor if it hasn't been cloned yet if (!mp.containsKey(neighbor)) { mp.put(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.offer(neighbor); } // Add the clone of the neighbor to the current node's clone mp.get(current).neighbors.add(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node2 node3))); node2.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node3))); node3.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node2 node4))); node4.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node3))); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static boolean compareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || n1 == n2) return false; visited.put(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.size() != n2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node neighbor1 = n1.neighbors.get(i); Node neighbor2 = n2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) != neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); boolean isEqual = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
from collections import deque # Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0): self.val = val self.neighbors = [] # Clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): if not node: return None # Map to hold original nodes as keys and their clones as values mp = {} # Initialize BFS queue q = deque([node]) # Clone the starting node mp[node] = Node(node.val) while q: current = q.popleft() for neighbor in current.neighbors: # If neighbor not cloned yet if neighbor not in mp: mp[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val) q.append(neighbor) # Link clone of neighbor to the clone of the current node mp[current].neighbors.append(mp[neighbor]) return mp[node] # Build graph def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs structurally and by values def compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): if not n1 or not n2: return n1 == n2 if n1.val != n2.val or n1 is n2: return False visited[n1] = n2 if len(n1.neighbors) != len(n2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(n1.neighbors)): neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i] neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i] if neighbor1 in visited: if visited[neighbor1] != neighbor2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited): return False return True # Driver if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() cloned = cloneGraph(original) result = compareGraphs(original cloned {}) print('true' if result else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Definition for a Node public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; var mp = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); var q = new Queue<Node>(); // Clone the starting node var clone = new Node(node.val); mp[node] = clone; q.Enqueue(node); while (q.Count > 0) { var current = q.Dequeue(); foreach (var neighbor in current.neighbors) { // If neighbor not cloned clone it and enqueue if (!mp.ContainsKey(neighbor)) { mp[neighbor] = new Node(neighbor.val); q.Enqueue(neighbor); } // Add clone of neighbor to clone of current mp[current].neighbors.Add(mp[neighbor]); } } return mp[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { var node1 = new Node(0); var node2 = new Node(1); var node3 = new Node(2); var node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node2 node3 }); node2.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node3 }); node3.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node2 node4 }); node4.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node3 }); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static bool CompareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || ReferenceEquals(n1 n2)) return false; visited[n1] = n2; if (n1.neighbors.Count != n2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.Count; i++) { var neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; var neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(neighbor1)) { if (!ReferenceEquals(visited[neighbor1] neighbor2)) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void Main() { var original = BuildGraph(); var cloned = CloneGraph(original); var visited = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); Console.WriteLine(CompareGraphs(original cloned visited) ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Clone the graph function cloneGraph(node) { if (!node) return null; const mp = new Map(); const q = [node]; // Clone the initial node mp.set(node new Node(node.val)); while (q.length > 0) { const current = q.shift(); for (const neighbor of current.neighbors) { if (!mp.has(neighbor)) { mp.set(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.push(neighbor); } // Link clone of neighbor to clone of current mp.get(current).neighbors.push(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors = [node2 node3]; node2.neighbors = [node1 node3]; node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4]; node4.neighbors = [node3]; return node1; } // Compare two graphs structurally and by value function compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited = new Map()) { if (!n1 || !n2) return n1 === n2; if (n1.val !== n2.val || n1 === n2) return false; visited.set(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.length !== n2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.length; i++) { const neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; const neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) !== neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver const original = buildGraph(); const cloned = cloneGraph(original); const result = compareGraphs(original cloned); console.log(result ? 'true' : 'false');
Výstup
true
[Prístup 2] Použitie prechodu DFS – čas O(V+E) a priestor O(V)
C++V prístupe DFS je graf klonovaný pomocou rekurzie. Začneme od daného uzla a pred návratom preskúmame čo najďalej pozdĺž každej vetvy. Mapa (alebo slovník) sa používa na sledovanie už klonovaných uzlov, aby sa predišlo viacnásobnému spracovaniu toho istého uzla a spracovaniu cyklov. Keď sa s uzlom stretneme prvýkrát, vytvoríme jeho klon a uložíme ho na mapu. Potom pre každého suseda tohto uzla rekurzívne naklonujeme a pridáme klonovaného suseda do klonu aktuálneho uzla. To zaisťuje, že všetky uzly sú pred návratom hlboko navštívené a štruktúra grafu je verne skopírovaná.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { int val; ArrayList<Node> neighbors; Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Map to hold original node to its copy static HashMap<Node Node> copies = new HashMap<>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.containsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies.put(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node2 node3)); node2.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1 node3)); node3.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1node2 node4)); node4.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node3)); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static boolean compareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited.put(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.size() != node2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors.get(i); Node n2 = node2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) != n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph boolean result = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(result ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
# Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0 neighbors=None): self.val = val self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else [] # Map to hold original node to its copy copies = {} # Function to clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): # If the node is None return None if not node: return None # If node is not yet cloned clone it if node not in copies: # Create a clone of the node clone = Node(node.val) copies[node] = clone # Recursively clone neighbors for neighbor in node.neighbors: clone.neighbors.append(cloneGraph(neighbor)) # Return the clone return copies[node] def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs for structural and value equality def compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited): if not node1 or not node2: return node1 == node2 if node1.val != node2.val or node1 is node2: return False visited[node1] = node2 if len(node1.neighbors) != len(node2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(node1.neighbors)): n1 = node1.neighbors[i] n2 = node2.neighbors[i] if n1 in visited: if visited[n1] != n2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): return False return True # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() # Clone the graph using DFS cloned = cloneGraph(original) # Compare original and cloned graph visited = {} print('true' if compareGraphs(original cloned visited) else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Dictionary to hold original node to its copy static Dictionary<Node Node> copies = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.ContainsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies[node] = clone; // Recursively clone neighbors foreach (Node neighbor in node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.Add(CloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.Add(node2); node1.neighbors.Add(node3); node2.neighbors.Add(node1); node2.neighbors.Add(node3); node3.neighbors.Add(node1); node3.neighbors.Add(node2); node3.neighbors.Add(node4); node4.neighbors.Add(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static bool CompareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited[node1] = node2; if (node1.neighbors.Count != node2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.Count; i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; Node n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(n1)) { if (visited[n1] != n2) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { Node original = BuildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS Node cloned = CloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph bool isEqual = CompareGraphs(original cloned new Dictionary<Node Node>()); Console.WriteLine(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Map to hold original node to its copy const copies = new Map(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS function cloneGraph(node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node === null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.has(node)) { const clone = new Node(node.val); copies.set(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (let neighbor of node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.push(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.push(node2 node3); node2.neighbors.push(node1 node3); node3.neighbors.push(node1 node2 node4); node4.neighbors.push(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality function compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited = new Map()) { if (!node1 || !node2) return node1 === node2; if (node1.val !== node2.val || node1 === node2) return false; visited.set(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.length !== node2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.length; i++) { const n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; const n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) !== n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code const original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS const cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph console.log(compareGraphs(original cloned) ? 'true' : 'false');
Výstup
true