V tomto článku budeme diskutovať o algoritme Quicksort. Jednoduchý je aj pracovný postup Quicksortu. Tento článok bude pre študentov veľmi užitočný a zaujímavý, pretože pri skúškach môžu čeliť rýchlemu triedeniu ako otázke. Preto je dôležité diskutovať o téme.
Triedenie je spôsob systematického usporiadania položiek. Quicksort je široko používaný triediaci algoritmus n log n porovnania v priemernom prípade triedenia poľa n prvkov. Je to rýchlejší a vysoko efektívny triediaci algoritmus. Tento algoritmus sa riadi prístupom rozdeľuj a panuj. Rozdeľuj a panuj je technika rozdelenia algoritmov na podproblémy, potom riešenie podproblémov a spájanie výsledkov späť, aby sa vyriešil pôvodný problém.
maven nainštalovať
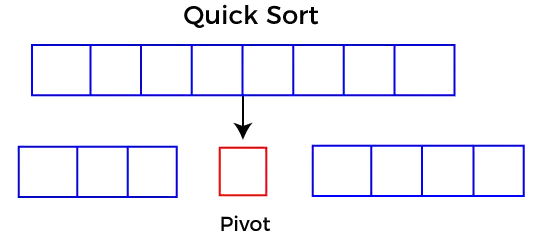
Rozdeliť: V časti Rozdeliť najprv vyberte otočný prvok. Potom rozdeľte alebo preusporiadajte pole na dve čiastkové polia tak, aby každý prvok v ľavom čiastkovom poli bol menší alebo rovný pivotnému prvku a každý prvok v pravom podpole bol väčší ako pivotový prvok.
dobyť: Rekurzívne zoraďte dve podpolia pomocou Quicksort.
Kombinovať: Skombinujte už zoradené pole.
Quicksort vyberie prvok ako pivot a potom rozdelí dané pole okolo vybratého prvku pivota. Pri rýchlom zoradení je veľké pole rozdelené na dve polia, z ktorých jedno obsahuje hodnoty, ktoré sú menšie ako zadaná hodnota (Pivot), a ďalšie pole obsahuje hodnoty, ktoré sú väčšie ako pivot.
Potom sa pomocou rovnakého prístupu rozdelí aj ľavé a pravé podpole. Bude to pokračovať, kým jediný prvok nezostane v podskupine.
Výber pivota
Výber dobrého pivota je nevyhnutný pre rýchlu implementáciu rýchleho triedenia. Typické je však určiť dobrého pivota. Niektoré zo spôsobov výberu pivotu sú nasledovné -
- Pivot môže byť náhodný, t.j. vybrať náhodný pivot z daného poľa.
- Pivot môže byť buď prvok úplne vpravo alebo prvok úplne vľavo daného poľa.
- Ako prvok pivot vyberte medián.
Algoritmus
Algoritmus:
QUICKSORT (array A, start, end) { 1 if (start <end) 2 3 4 5 6 { p="partition(A," start, end) quicksort (a, - 1) + 1, } < pre> <p> <strong>Partition Algorithm:</strong> </p> <p>The partition algorithm rearranges the sub-arrays in a place.</p> <pre> PARTITION (array A, start, end) { 1 pivot ? A[end] 2 i ? start-1 3 for j ? start to end -1 { 4 do if (A[j] <pivot) 1 5 6 7 8 9 { then i ? + swap a[i] with a[j] }} a[i+1] a[end] return i+1 } < pre> <h2>Working of Quick Sort Algorithm</h2> <p>Now, let's see the working of the Quicksort Algorithm.</p> <p>To understand the working of quick sort, let's take an unsorted array. It will make the concept more clear and understandable.</p> <p>Let the elements of array are -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-2.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>In the given array, we consider the leftmost element as pivot. So, in this case, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 27 and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right and move towards left.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-3.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves forward one position towards left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-4.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 19, and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Because, a[pivot] > a[right], so, algorithm will swap a[pivot] with a[right], and pivot moves to right, as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-5.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 19, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. Since, pivot is at right, so algorithm starts from left and moves to right.</p> <p>As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-6.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 9, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-7.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 29, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[left], so, swap a[pivot] and a[left], now pivot is at left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-8.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right, and move to left. Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 29, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves one position to left, as -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-9.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 14. As a[pivot] > a[right], so, swap a[pivot] and a[right], now pivot is at right, i.e. -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-10.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 14, and a[right] = 24. Pivot is at right, so the algorithm starts from left and move to right.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-11.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 24. So, pivot, left and right are pointing the same element. It represents the termination of procedure.</p> <p>Element 24, which is the pivot element is placed at its exact position.</p> <p>Elements that are right side of element 24 are greater than it, and the elements that are left side of element 24 are smaller than it.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-12.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, in a similar manner, quick sort algorithm is separately applied to the left and right sub-arrays. After sorting gets done, the array will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-13.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <h2>Quicksort complexity</h2> <p>Now, let's see the time complexity of quicksort in best case, average case, and in worst case. We will also see the space complexity of quicksort.</p> <h3>1. Time Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>Case</th> <th>Time Complexity</th> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Best Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Average Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Worst Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Best Case Complexity -</td> In Quicksort, the best-case occurs when the pivot element is the middle element or near to the middle element. The best-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Average Case Complexity -</td> It occurs when the array elements are in jumbled order that is not properly ascending and not properly descending. The average case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Worst Case Complexity -</td> In quick sort, worst case occurs when the pivot element is either greatest or smallest element. Suppose, if the pivot element is always the last element of the array, the worst case would occur when the given array is sorted already in ascending or descending order. The worst-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</strong> . </tr></ul> <p>Though the worst-case complexity of quicksort is more than other sorting algorithms such as <strong>Merge sort</strong> and <strong>Heap sort</strong> , still it is faster in practice. Worst case in quick sort rarely occurs because by changing the choice of pivot, it can be implemented in different ways. Worst case in quicksort can be avoided by choosing the right pivot element.</p> <h3>2. Space Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <td> <strong>Space Complexity</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Stable</strong> </td> <td>NO</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The space complexity of quicksort is O(n*logn).</li> </ul> <h2>Implementation of quicksort</h2> <p>Now, let's see the programs of quicksort in different programming languages.</p> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in C language.</p> <pre> #include /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 27 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) printf('%d ', a[i]); main() 24, 9, 29, 14, 19, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); printf('before sorting elements are
'); printarr(a, n); 0, printf('
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-14.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in C++ language.</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 26 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) cout< <a[i]<< ' '; main() 23, 8, 28, 13, 18, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); cout<<'before sorting elements are
'; printarr(a, n); 0, cout<<'
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-15.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in python.</p> <pre> #function that consider last element as pivot, #place the pivot at its exact position, and place #smaller elements to left of pivot and greater #elements to right of pivot. def partition (a, start, end): i = (start - 1) pivot = a[end] # pivot element for j in range(start, end): # If current element is smaller than or equal to the pivot if (a[j] <= 1 pivot): i="i" + a[i], a[j]="a[j]," a[i] a[i+1], a[end]="a[end]," a[i+1] return (i 1) # function to implement quick sort def quick(a, start, end): a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, end="Ending" index if (start < p="partition(a," end) is partitioning - 1, printarr(a): print the array for in range(len(a)): (a[i], ) a="[68," 13, 49, 58] print('before sorting elements are ') printarr(a) 0, len(a)-1) print('
after pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-16.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in Java.</p> <pre> public class Quick { /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 25 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) system.out.print(a[i] ' '); public static main(string[] args) 13, 18, 27, 2, 19, }; n="a.length;" system.out.println('
before sorting elements are q1="new" quick(); q1.printarr(a, n); q1.quick(a, 0, system.out.println('
after system.out.println(); pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-17.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in php.</p> <pre> <?php /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ function partition (&$a, $start, $end) { $pivot = $a[$end]; // pivot element $i = ($start - 1); for ($j = $start; $j <= $end - 1; $j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if ($a[$j] < $pivot) { $i++; // increment index of smaller element $t = $a[$i]; $a[$i] = $a[$j]; $a[$j] = $t; } } $t = $a[$i+1]; $a[$i+1] = $a[$end]; $a[$end] = $t; return ($i + 1); } /* function to implement quick sort */ function quick(&$a, $start, $end) /* a[] = array to be sorted, start = Starting index, end = Ending index */ { if ($start < $end) { $p = partition($a, $start, $end); //p is partitioning index quick($a, $start, $p - 1); quick($a, $p + 1, $end); } } function printArray($a, $n) { for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) { print_r($a[$i]); echo ' '; } } $a = array( 89, 47, 2, 17, 8, 19 ); $n = count($a); echo 'Before sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); quick($a, 0, $n - 1); echo ' <br> After sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); ?> </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-18.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>So, that's all about the article. Hope the article will be helpful and informative to you.</p> <p>This article was not only limited to the algorithm. Along with the algorithm, we have also discussed the quick sort complexity, working, and implementation in different programming languages.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></a[right],></p></a[left],></p></a[right],></p></pivot)></pre></end)> Výkon
Po vykonaní vyššie uvedeného kódu bude výstupom -

Tak, to je o článku všetko. Dúfam, že článok bude pre vás užitočný a poučný.
okno.otvoriť
Tento článok nebol obmedzený len na algoritmus. Spolu s algoritmom sme diskutovali aj o zložitosti rýchleho triedenia, práci a implementácii v rôznych programovacích jazykoch.
