Daný obdĺžnikový papier rozmerov a x b . Úlohou je rozrezať celý papier minimálne počet štvorec kusov. Môžeme si vybrať štvorcové kusy akejkoľvek veľkosti, ale musia byť narezané bez prekrývania alebo zanechávania akéhokoľvek priestoru navyše .
Príklady:
Vstup: a = 5 b = 8
5 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 5 X 8
výstup: 5
Vysvetlenie: Papier môžeme rozrezať na 5 štvorcov: 1 štvorec veľkosti 5x5 1 štvorec veľkosti 3x3 1 štvorec veľkosti 2x2 a 2 štvorce veľkosti 1x1.Vstup: a = 13 b = 11
6 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 13 X 11
výstup: 6
Vysvetlenie: Papier môžeme rozrezať na 6 štvorcov: 1 štvorec veľkosti 7x7 1 štvorec veľkosti 6x6 1 štvorec veľkosti 5x5 2 štvorce veľkosti 4x4 a 1 štvorec veľkosti 1x1.Vstup: a = 6 b = 7
5 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 6 X 7
výstup: 5
Vysvetlenie: Papier môžeme rozrezať na 5 štvorcov: 1 štvorec veľkosti 4x4 2 štvorce veľkosti 3x3 a 2 štvorce veľkosti 3x3.
Obsah
- [Nesprávny prístup 1] Použitie nenásytnej techniky
- [Nesprávny prístup 2] Použitie dynamického programovania
- [Správny prístup] Použitie DFS a dynamického programovania
[Nesprávny prístup 1] Použitie nenásytnej techniky
Na prvý pohľad by sa mohlo zdať, že problém sa dá jednoducho vyriešiť tak, že z papiera najprv vystrihneme čo najväčší štvorec, potom zo zvyšného papiera odrežeme najväčší štvorec a tak ďalej, až kým nevystrihneme celý papier. Toto riešenie je ale nesprávne.
Prečo Greedy Approach nefunguje?
Zvážte papier veľkosti 6x7 ak sa potom pokúsime hltavo rezať papier, dostaneme 7 štvorce: 1 štvorec veľkosti 6x6 a 6 štvorcov veľkosti 1x1 pričom správne riešenie je: 5. Zištný prístup teda nebude fungovať.
[Nesprávny prístup 2] Použitie dynamického programovania
Dynamické programovanie s vertikálnymi alebo horizontálnymi rezmi: Ďalším riešením, ktoré sa môže zdať správne, je použitie Dynamické programovanie . Môžeme udržiavať tabuľku dp[][] takú, že dp[i][j] = minimálny počet štvorcov, ktoré je možné vyrezať z papiera veľkosti i x j . Potom pre papier veľkosti axb
- Môžeme to skúsiť odrezať pozdĺž každého riadku: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) kde k môže byť v rozsahu [1 i - 1].
- Môžeme to skúsiť orezať pozdĺž každého stĺpca: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) kde k môže byť v rozsahu [1 j - 1].
Nakoniec bude odpoveďou minimum všetkých rezov. Ale toto riešenie je tiež nesprávne.
Prečo rezanie vertikálne alebo horizontálne s prístupom dynamického programovania nefunguje?
Toto nebude fungovať, pretože predpokladáme, že zvislý alebo vodorovný rez vždy rozdelí obdĺžnik na dve časti. Zvážte papier veľkosti 13x11 potom, ak sa pokúsime orezať papier pomocou DP prístupu, dostaneme 8 štvorcov, ale správna odpoveď (ako je uvedené v príkladoch) je 6. Dynamické programovanie teda nebude fungovať.
[Správny prístup] Použitie DFS a dynamického programovania
C++The nápad je orezať celý papier pomocou DFS v zdola nahor spôsobom. V každom kroku nájdite najnižší ľavý roh papiera a pokúste sa z tohto rohu vyrezať štvorce všetkých možných veľkostí. Po vyrezaní štvorca opäť nájdite najnižší ľavý roh zostávajúceho papiera, aby ste mohli vyrezať štvorce všetkých možných veľkostí atď. Ak by sme však vyskúšali všetky možné výrezy z ľavého najnižšieho rohu každej možnej veľkosti papiera, bolo by to dosť neefektívne. Môžeme ho optimalizovať pomocou Dynamické programovanie na uloženie minimálnych rezov pre každú možnú veľkosť papiera.
Aby sme jednoznačne identifikovali akúkoľvek veľkosť papiera, môžeme udržiavať pole remSq[] tak, že remSq[i] ukladá počet zostávajúcich štvorcov veľkosti 1x1 v itom stĺpci papiera. Takže pre papier veľkosti 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Aby sme našli ľavý najnižší roh, nájdeme prvý index s maximálnym počtom zostávajúcich štvorcov. Takže môžeme hashovať hodnotu poľa remSq[], aby sme našli jedinečný kľúč pre všetky možné hodnoty poľa remSq[].
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Výstup
6
Časová zložitosť: O(a^b) pre každý z b stĺpcov môžeme mať štvorce.
Pomocný priestor: O(a^b) vďaka memoizácii, ktorá ukladá každý jedinečný stav.

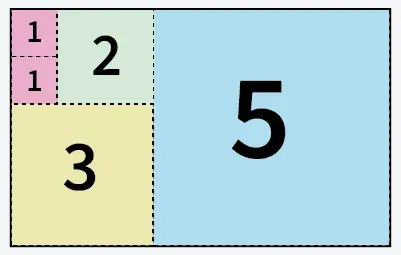 5 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 5 X 8
5 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 5 X 8 6 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 13 X 11
6 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 13 X 11 5 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 6 X 7
5 štvorcov vyrezaných z papiera veľkosti 6 X 7