The slučka for v jazyku C sa používa na niekoľkonásobné opakovanie príkazov alebo časti programu. Často sa používa na prechádzanie dátovými štruktúrami, ako je pole a prepojený zoznam.
Syntax cyklu for v jazyku C
Syntax cyklu for v jazyku c je uvedená nižšie:
pripojiť databázu java
for(Expression 1; Expression 2; Expression 3){ //code to be executed } Vývojový diagram cyklu for v jazyku C
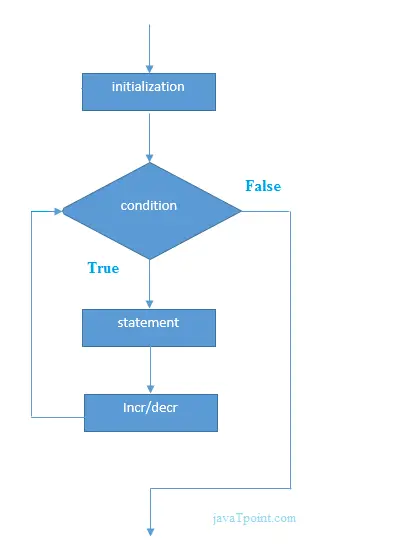
C pre príklady slučky
Pozrime sa na jednoduchý program cyklu for, ktorý vypíše tabuľku 1.
#include int main(){ int i=0; for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',i); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 </pre> <h3>C Program: Print table for the given number using C for loop</h3> <pre> #include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf('%d ',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf('%d %d %d
',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf('%d %d
',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){></pre></=10;i++){> Program C: Tlač tabuľky pre dané číslo pomocou cyklu C for
#include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf(\'%d
\',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
Vlastnosti výrazu 1
- Výraz predstavuje inicializáciu premennej cyklu.
- Vo výraze 1 môžeme inicializovať viac ako jednu premennú.
- Výraz 1 je voliteľný.
- V C nemôžeme deklarovať premenné vo výraze 1. V niektorých kompilátoroch to však môže byť výnimka.
Príklad 1
#include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)> Príklad 2
#include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)> Vlastnosti výrazu 2
- Výraz 2 je podmienený výraz. Kontroluje, či je splnená konkrétna podmienka. Ak nie je, cyklus sa ukončí.
- Výraz 2 môže mať viac ako jednu podmienku. Cyklus sa však bude opakovať, kým sa posledná podmienka nestane nepravdivou. Ostatné podmienky sa budú považovať za vyhlásenia.
- Výraz 2 je voliteľný.
- Výraz 2 môže vykonávať úlohu výrazu 1 a výrazu 3. To znamená, že môžeme inicializovať premennú, ako aj aktualizovať premennú cyklu v samotnom výraze 2.
- Vo výraze 2 môžeme zadať nulovú alebo nenulovú hodnotu. V jazyku C je však každá nenulová hodnota pravdivá a nula je štandardne nepravda.
Príklad 1
zložený kľúč primárneho kľúča
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)> Príklad 2
#include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\\'%d %d %d
\\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)> Príklad 3
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } Výkon
infinite loop
Vlastnosti výrazu 3 - Výraz 3 sa používa na aktualizáciu premennej cyklu.
- Môžeme aktualizovať viac ako jednu premennú súčasne.
- Výraz 3 je voliteľný.
Príklad 1
previesť bajtové pole na reťazec
#include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)> Telo slučky
Zátvorky {} sa používajú na definovanie rozsahu cyklu. Ak však cyklus obsahuje iba jeden príkaz, potom nemusíme používať zátvorky. Slučka bez tela je možná. Zložené zátvorky fungujú ako oddeľovač blokov, t. j. premenná hodnota deklarovaná vo vnútri cyklu for je platná len pre tento blok a nie vonku. Zvážte nasledujúci príklad.
#include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)> Infinitív for slučky v C
Aby bol cyklus for nekonečný, nemusíme v syntaxi uvádzať žiadny výraz. Namiesto toho musíme poskytnúť dve bodkočiarky na overenie syntaxe cyklu for. Toto bude fungovať ako nekonečný cyklus for.
#include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } Ak spustíte tento program, uvidíte vyššie uvedený príkaz nekonečne krát.
