Vzhľadom na dva reťazce, S1 a S2 , úlohou je nájsť dĺžku najdlhšej spoločnej podsekvencie, t.j. najdlhšej podsekvencie prítomnej v oboch reťazcoch.
A najdlhšia spoločná podsekvencia (LCS) je definovaná ako najdlhšia podsekvencia, ktorá je spoločná pre všetky dané vstupné sekvencie.
Najdlhšia spoločná sekvencia
Príklady:
Odporúčaná prax Najdlhšia bežná následná sekvencia Vyskúšajte to!Vstup: S1 = ABC, S2 = ACD
Výkon: 2
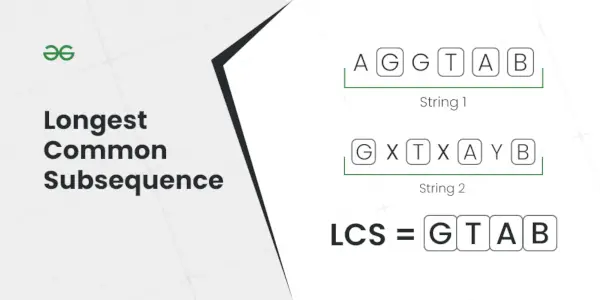
Vysvetlenie: Najdlhšia podsekvencia, ktorá je prítomná v oboch reťazcoch, je AC.Vstup: S1 = AGGTAB, S2 = GXTXAYB
Výkon: 4
Vysvetlenie: Najdlhšia spoločná subsekvencia je GTAB.Vstup: S1 = ABC, S2 = CBA
Výkon: 1
Vysvetlenie: Existujú tri spoločné podsekvencie dĺžky 1, A, B a C a žiadna spoločná podsekvencia s dĺžkou väčšou ako 1.Vstup: S1 = XYZW, S2 = XYWZ
Výkon: 3
Vysvetlenie: Existujú dve spoločné podsekvencie dĺžky 3 XYZ a XYW a žiadna spoločná podsekvencia. s dĺžkou viac ako 3.dlhý na reťazec java
Najdlhšia spoločná podsekvencia (LCS) pomocou rekurzie:
Vygenerujte všetky možné podsekvencie a nájdite z nich najdlhšiu, ktorá je prítomná v oboch reťazcoch pomocou Pri implementácii myšlienky postupujte podľa nasledujúcich krokov:
- Vytvorte rekurzívnu funkciu [povedzme lcs() ].
- Skontrolujte vzťah medzi prvými znakmi reťazcov, ktoré ešte nie sú spracované.
- V závislosti od vzťahu zavolajte ďalšiu rekurzívnu funkciu, ako je uvedené vyššie.
- Vráťte dĺžku prijatého LCS ako odpoveď.
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia rekurzívneho prístupu:
C++C// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra>Java// A Naive recursive implementation // of LCS problem #include int max(int a, int b); // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int i, int j) // Utility function to get max of // 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b) ? a: b; } // Kód ovládača int main() { char S1[] = 'BD'; char S2[] = 'ABCD'; int m = strlen(S1); int n = strlen(S2); int i = 0, j = 0; // Volanie funkcie printf('Dlzka LCS je %d', lcs(S1, S2, i, j)); návrat 0; }>Python// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem in java import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) n == 0) return 0; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1); else return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n)); // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b) ? a: b; } // Kód ovládača public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence(); Reťazec S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Reťazec S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.dlzka(); int n = S2.dlzka(); System.out.println('Dĺžka LCS je' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Tento kód pridal Saket Kumar>C## A Naive recursive Python implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): if m == 0 or n == 0: return 0 elif X[m-1] == Y[n-1]: return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m-1, n-1) else: return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n-1), lcs(X, Y, m-1, n)) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, len(S1), len(S2)))>Javascript// C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) if (m == 0 // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b) ? a: b; } // Kód ovládača public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Reťazec S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Dĺžka; int n = S2.Dĺžka; Console.Write('Dĺžka LCS je' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Tento kód vytvoril Sam007>PHP>
VýkonLength of LCS is 4>Časová zložitosť: O(2m+n)
Pomocný priestor: O(1)Použitie najdlhšej spoločnej subsekvencie (LCS). Zapamätanie :
1. Optimálna spodná štruktúra:
Pozri na riešenie štruktúry L(X[0, 1, . . ., m-1], Y[0, 1, . . . , n-1]), na pomoc si berieme podštruktúry X[0 , 1, …, m-2], Y[0, 1,…, n-2], v závislosti od situácie (t. j. ich optimálneho využitia) nájsť riešenie celku.
iterovať cez mapu java2. Prekrývajúce sa čiastkové problémy:
Ak použijeme vyššie uvedený rekurzívny prístup pre reťazce BD a A B C D , dostaneme strom čiastočnej rekurzie, ako je uvedené nižšie. Tu vidíme, že podproblém L(BD, ABCD) sa počíta viackrát. Ak vezmeme do úvahy celkový strom, bude existovať niekoľko takýchto prekrývajúcich sa čiastkových problémov.
L(AXYT, AYZX)
/
L(AXY, AYZX) L(AXYT, AYZ)
/ /
L(AX, AYZX) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXYT, AY)Prístup: Vďaka prítomnosti týchto dvoch vlastností môžeme na vyriešenie problému použiť dynamické programovanie alebo memoizáciu. Nižšie je uvedený prístup k riešeniu pomocou rekurzie.
- Vytvorte rekurzívnu funkciu. Vytvorte tiež 2D pole na uloženie výsledku jedinečného stavu.
- Ak sa počas rekurzného volania zavolá rovnaký stav viackrát, môžeme priamo vrátiť odpoveď uloženú pre tento stav namiesto opätovného výpočtu.
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia vyššie uvedeného prístupu:
C++Java// A Top-Down DP implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int m, int n, vector>& dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) návrat dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } // Kód ovládača int main() { char X[] = 'AGGTAB'; char Y[] = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = strlen(X); int n = strlen(Y); vektor > dp(m + 1, vektor (n + 1, -1)); cout<< 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp); return 0; }> Python/*package whatever //do not write package name here */ import java.io.*; class GFG { // A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n, int[][] dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (dp[m][n] != -1) return dp[m][n]; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) { dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); return dp[m][n]; } dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); return dp[m][n]; } // Drivers code public static void main(String args[]) { String X = 'AGGTAB'; String Y = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = X.length(); int n = Y.length(); int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) { dp[i][j] = -1; } } System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); } } // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>C## A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem # Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] def lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp): if (m == 0 or n == 0): return 0 if (dp[m][n] != -1): return dp[m][n] if X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]: dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp) return dp[m][n] dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)) return dp[m][n] # Driver code X = 'AGGTAB' Y = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(X) n = len(Y) dp = [[-1 for i in range(n + 1)]for j in range(m + 1)] print(f'Length of LCS is {lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)}') # This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>Javascript/* C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem */ using System; class GFG { /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ static int lcs(char[] X, char[] Y, int m, int n, int[, ] L) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (L[m, n] != -1) return L[m, n]; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) { L[m, n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, L); return L[m, n]; } L[m, n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, L), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, L)); return L[m, n]; } /* Utility function to get max of 2 integers */ static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b) ? a: b; } public static void Main() { String s1 = 'AGGTAB'; Reťazec s2 = 'GXTXAYB'; char[] X = s1.ToCharArray(); char[] Y = s2.ToCharArray(); int m = X. Dĺžka; int n = Y. Dĺžka; int[, ] L = nový int[m + 1, n + 1]; pre (int i = 0; i<= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { L[i, j] = -1; } } Console.Write('Length of LCS is' + ' ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, L)); } } // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>/* A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem */ /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ function lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) return dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } /* Driver code */ let X = 'AGGTAB'; let Y = 'GXTXAYB'; let m = X.length; let n = Y.length; let dp = new Array(m + 1); for(let i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { dp[i] = new Array(n + 1).fill(-1); } console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>
VýkonLength of LCS is 4>Časová zložitosť: O(m * n) kde m a n sú dĺžky reťazcov.
Pomocný priestor: O(m * n) Tu sa ignoruje rekurzívny zásobníkový priestor.Najdlhšia spoločná sekvencia (LCS) pomocou zdola nahor (tabuľka):
Na implementáciu prístupu dynamického programovania pre LCS môžeme použiť nasledujúce kroky.
- Vytvorte 2D pole dp[][] s riadkami a stĺpcami rovnými dĺžke každého vstupného reťazca plus 1 [počet riadkov označuje indexy S1 a stĺpce označujú indexy S2 ].
- Inicializujte prvý riadok a stĺpec poľa dp na 0.
- Iterujte cez riadky poľa dp, začínajúc od 1 (povedzme pomocou iterátora i ).
- Pre každý i , iterujte všetky stĺpce z j = 1 až n :
- Ak S1[i-1] rovná sa S2[j-1] , nastavte aktuálny prvok poľa dp na hodnotu prvku na ( dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 ).
- V opačnom prípade nastavte aktuálny prvok poľa dp na maximálnu hodnotu dp[i-1][j] a dp[i][j-1] .
- Po vnorených slučkách bude posledný prvok poľa dp obsahovať dĺžku LCS.
Pre lepšie pochopenie si pozrite nasledujúci obrázok:
Ilustrácia:
Povedzme, že struny sú S1 = AGGTAB a S2 = GXTXAYB .
Prvý krok: Najprv vytvorte 2D maticu (povedzme dp[][]) s veľkosťou 8 x 7, ktorej prvý riadok a prvý stĺpec sú vyplnené 0.
Vytvorenie tabuľky dp
Druhý krok: Prechod pre i = 1. Keď sa j stane 5, S1[0] a S2[4] sú rovnaké. Takže dp[][] sa aktualizuje. Pre ostatné prvky vezmite maximum dp[i-1][j] a dp[i][j-1]. (V tomto prípade, ak sú obe hodnoty rovnaké, použili sme šípky na predchádzajúce riadky).
Vyplňte riadok číslo 1
Tretí krok: Pri prechode pre i = 2 sú S1[1] a S2[0] rovnaké (obe sú „G“). Hodnota dp v tejto bunke sa teda aktualizuje. Ostatné prvky sú aktualizované podľa podmienok.
tiger v porovnaní s levomVyplnenie riadku č. 2
Štvrtý krok: Pre i = 3 sú S1[2] a S2[0] opäť rovnaké. Aktualizácie sú nasledovné.
Vyplnenie riadku č. 3
Piaty krok: Pre i = 4 môžeme vidieť, že S1[3] a S2[2] sú rovnaké. Takže dp[4][3] aktualizované ako dp[3][2] + 1 = 2.
Vyplnenie riadku 4
Šiesty krok: Tu vidíme, že pre i = 5 a j = 5 sú hodnoty S1[4] a S2[4] rovnaké (t.j. obe sú „A“). Takže dp[5][5] sa zodpovedajúcim spôsobom aktualizuje a stane sa 3.
Vyplnenie riadku 5
Posledný krok: Pre i = 6 si pozrite, že posledné znaky oboch reťazcov sú rovnaké (sú to „B“). Preto hodnota dp[6][7] bude 4.
Vyplnenie posledného riadku
program dvojrozmerného poľa v cDostaneme teda maximálnu dĺžku spoločnej podsekvencie as 4 .
Nasleduje tabuľková implementácia pre problém LCS.
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) { // Initializing a matrix of size // (m+1)*(n+1) int L[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. Note that // L[i][j] contains length of LCS of // X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) if (i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains length of LCS // for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n]; } // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; }>Python// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int L[][] = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up // fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS // of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X.charAt(i - 1) == Y.charAt(j - 1)) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } return L[m][n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b) ? a: b; } public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence(); Reťazec S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Reťazec S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.dlzka(); int n = S2.dlzka(); System.out.println('Dĺžka LCS je' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Tento kód pridal Saket Kumar>C## Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): # Declaring the array for storing the dp values L = [[None]*(n+1) for i in range(m+1)] # Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion # Note: L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1] # and Y[0..j-1] for i in range(m+1): for j in range(n+1): if i == 0 or j == 0: L[i][j] = 0 elif X[i-1] == Y[j-1]: L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1]+1 else: L[i][j] = max(L[i-1][j], L[i][j-1]) # L[m][n] contains the length of LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n] # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(S1) n = len(S2) print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, m, n)) # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)>Javascript// Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int[, ] L = new int[m + 1, n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. // Note that L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i, j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i, j] = L[i - 1, j - 1] + 1; else L[i, j] = max(L[i - 1, j], L[i, j - 1]); } return L[m, n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b) ? a: b; } // Kód ovládača public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Reťazec S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Dĺžka; int n = S2.Dĺžka; Console.Write('Dĺžka LCS je' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Tento kód pridal Sam007>PHP// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem // Utility function to get max of 2 integers function max(a, b) { if (a>b) vrátiť a; inak vrátiť b; } // Vráti dĺžku LCS pre funkciu X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] lcs(X, Y, m, n) { var L = new Array(m + 1); for(var i = 0; i< L.length; i++) { L[i] = new Array(n + 1); } var i, j; /* Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] */ for(i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for(j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } /* L[m][n] contains length of LCS for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] */ return L[m][n]; } // Driver code var S1 = 'AGGTAB'; var S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; var m = S1.length; var n = S2.length; console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>// Dynamic Programming C# // implementation of LCS problem function lcs($X , $Y, $m, $n) { // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion . // Note: L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for ($i = 0; $i <= $m; $i++) { for ($j = 0; $j <= $n; $j++) if ($i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains the length of // LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return $L[$m][$n]; } // Driver Code $S1 = 'AGGTAB'; $S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; $m = strlen($S1); $n = strlen($S2) ; echo 'Length of LCS is '; echo lcs($S1, $S2, $m, $n); // This code is contributed // by Shivi_Aggarwal ?>>
VýkonLength of LCS is 4>Časová zložitosť: O(m * n), čo je oveľa lepšie ako časová zložitosť najhoršieho prípadu naivnej rekurzívnej implementácie.
Pomocný priestor: O(m * n), pretože algoritmus používa pole veľkosti (m+1)*(n+1) na uloženie dĺžky spoločných podreťazcov.Najdlhšia spoločná sekvencia (LCS) s použitím zdola nahor (optimalizácia priestoru):
- Vo vyššie uvedenom tabuľkovom prístupe používame L[i-1][j] a L[i][j] atď., tu L[i-1] bude odkazovať na predchádzajúci riadok matice L a L[i] sa týka aktuálny riadok.
- Optimalizáciu priestoru môžeme vykonať pomocou dvoch vektorov, jeden je predchádzajúci a druhý aktuálny.
- Keď sa vnútorná slučka for ukončí, inicializujeme predchádzajúce rovnaké ako aktuálne.
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia:
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; int longestCommonSubsequence(string& text1, string& text2) { int n = text1.size(); int m = text2.size(); // initializing 2 vectors of size m vectorprev(m + 1, 0), cur(m + 1, 0); for (int idx2 = 0; idx2< m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2); return 0; }> Python// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.Arrays; public class GFG { public static int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { int n = text1.length(); int m = text2.length(); // Initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If matching if (text1.charAt(idx1 - 1) == text2.charAt(idx2 - 1)) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // Not matching else cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = Arrays.copyOf(cur, m + 1); } return cur[m]; } public static void main(String[] args) { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; String S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>C#def longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2): n = len(text1) m = len(text2) # Initializing two lists of size m prev = [0] * (m + 1) cur = [0] * (m + 1) for idx1 in range(1, n + 1): for idx2 in range(1, m + 1): # If characters are matching if text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]: cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1] else: # If characters are not matching cur[idx2] = max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]) prev = cur.copy() return cur[m] if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' # Function call print('Length of LCS is', longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)) # This code is contributed by Rishabh Mathur>Javascriptusing System; class Program { static int LongestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int n = text1.Length; int m = text2.Length; // initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + Math.Max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } static void Main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call Console.WriteLine('Length of LCS is ' + LongestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>function longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2) { const n = text1.length; const m = text2.length; // Initializing two arrays of size m let prev = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); let cur = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); for (let idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { cur[idx2] = 0; } for (let idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (let idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If characters match if (text1[idx1 - 1] === text2[idx2 - 1]) { cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; } // If characters don't match else { cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } } // Update the 'prev' array prev = [...cur]; } return cur[m]; } // Main function function main() { const S1 = 'AGGTAB'; const S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call console.log('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } // Call the main function main();>
VýkonLength of LCS is 4>Časová zložitosť: O(m * n), ktoré zostáva rovnaké.
Pomocný priestor: O(m), pretože algoritmus používa dve polia veľkosti m.







