Vzhľadom na koreň a Binárny vyhľadávací strom a celé číslo k . Úlohou je nájsť najväčší počet v binárnom vyhľadávacom strome menej ako alebo rovný do k, ak takýto prvok neexistuje, print -1.
Príklady:
Vstup:
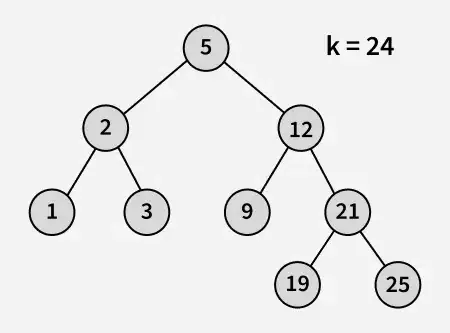
výstup: 21
vysvetlenie: 19 a 25 sú dve čísla najbližšie k 21 a 19 je najväčšie číslo s hodnotou menšou alebo rovnou 21.
Vstup: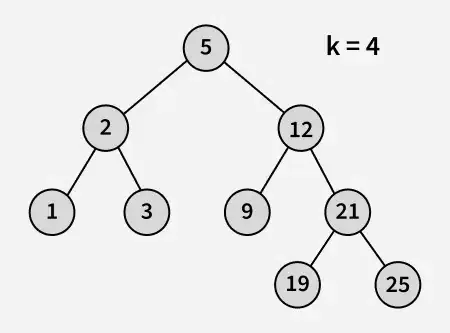
výstup: 3
vysvetlenie: 3 a 5 sú dve čísla najbližšie k 4 a 3 je najväčšie číslo s hodnotou menšou alebo rovnou 4.
Obsah
- [Naivný prístup] Použitie rekurzie - O(h) čas a O(h) priestor
- [Očakávaný prístup] Použitie iterácie - O(h) čas a O(1) priestor
[Naivný prístup] Použitie rekurzie - O(h) čas a O(h) priestor
C++Myšlienkou je začať na koreň a porovnaj jeho hodnotu s k. Ak je hodnota uzla väčšia ako k, prejdite do ľavého podstromu. V opačnom prípade nájdite hodnotu najväčšieho čísla menšiu ako k v pravý podstrom . Ak pravý podstrom vráti hodnotu -1 (čo znamená, že takáto hodnota neexistuje), vráti hodnotu aktuálneho uzla. Inak vráti hodnotu vrátenú pravým podstromom (pretože bude väčšia ako hodnota aktuálneho uzla, ale menšia ako rovná k).
ako previesť char na reťazec java
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): # Base cases if root is None: return -1 if root.data == k: return k # If root's value is smaller # try in right subtree elif root.data < k: x = findMaxFork(root.right k) if x == -1: return root.data else: return x # If root's data is greater # return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k) if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = FindMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return FindMaxFork(root.left k); } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { // Base cases if (root === null) return -1; if (root.data === k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { let x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x === -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Výstup
21
[Očakávaný prístup] Použitie iterácie - O(h) čas a O(1) priestor
C++Myšlienkou je začať na koreň a porovnať jeho hodnotu s k . Ak je hodnota uzla <= k aktualizujte výslednú hodnotu na hodnotu root a presuňte sa na správne podstrom inak presunúť do vľavo podstrom. Autor: iteratívne použitím tejto operácie naprieč všetkými uzlami môžeme minimalizovať priestor potrebný pre rekurzia zásobník.
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): result = -1 # Start from root and keep looking for larger while root is not None: # If root is smaller go to right side if root.data <= k: result = root.data root = root.right # If root is greater go to left side else: root = root.left return result if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { let result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root !== null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Výstup
21Vytvoriť kvíz


