V tomto článku uvidíme rôzne spôsoby zápisu do súboru pomocou programovacieho jazyka Java. Trieda Java FileWriter v jazyku Java sa používa na zápis znakovo orientovaných údajov do súboru, pretože táto trieda je trieda orientovaná na znaky kvôli tomu, čo sa používa pri manipulácii so súbormi v jazyku Java.
Je ich veľa spôsoby zápisu do súboru v jazyku Java pretože existuje veľa tried a metód, ktoré môžu splniť tento cieľ takto:
- Použitím writeString() metóda
- Použitie triedy FileWriter
- Použitie triedy BufferedWriter
- Pomocou triedy FileOutputStream
Metóda 1: Použitie metódy writeString().
Táto metóda je podporovaná verziou Java 11. Táto metóda môže mať štyri parametre. Ide o cestu k súboru, postupnosť znakov, znakovú sadu a možnosti. Prvé dva parametre sú povinné pre túto metódu na zápis do súboru. Zapisuje znaky ako obsah súboru. Vráti cestu k súboru a môže vyvolať štyri typy výnimiek. Je lepšie použiť, keď je obsah súboru krátky.
Príklad: Ukazuje použitie writeString() metóda, ktorá je v triede Files na zapisovanie údajov do súboru. Ďalšia trieda, Path, sa používa na priradenie názvu súboru s cestou, kde bude obsah zapísaný. Trieda Files má inú pomenovanú metódu readString() na čítanie obsahu akéhokoľvek existujúceho súboru, ktorý sa používa v kóde na kontrolu, či je obsah v súbore správne zapísaný.
Java
java hasnext
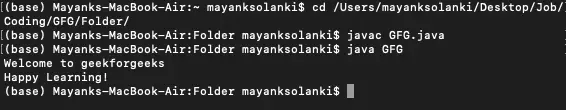
// Java Program to Write Into a File> // using writeString() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.IOException;> import> java.nio.file.Files;> import> java.nio.file.Path;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >throws> IOException> >{> >// Assigning the content of the file> >String text> >=>'Welcome to geekforgeeks
Happy Learning!'>;> >// Defining the file name of the file> >Path fileName = Path.of(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into the file> >Files.writeString(fileName, text);> >// Reading the content of the file> >String file_content = Files.readString(fileName);> >// Printing the content inside the file> >System.out.println(file_content);> >}> }> |
>
>Výkon
android proces acore
Welcome to geekforgeeks Happy Learning!>
Metóda 2: Použitie triedy FileWriter
Ak je obsah súboru krátky, ďalšou lepšou možnosťou je použitie triedy FileWriter na zápis do súboru. Zapisuje tiež prúd znakov ako obsah súboru, napríklad metóda writeString(). Konštruktor tejto triedy definuje predvolené kódovanie znakov a predvolenú veľkosť vyrovnávacej pamäte v bajtoch.
Nasledujúci príklad ilustruje použitie triedy FileWriter na zápis obsahu do súboru. Vyžaduje vytvorenie objektu triedy FileWriter s názvom súboru na zápis do súboru. Ďalej sa metóda write() používa na zápis hodnoty textovej premennej do súboru. Ak sa v čase zápisu súboru vyskytne chyba, vyvolá sa výnimka IOException a chybové hlásenie sa vytlačí z bloku catch.
Príklad:
Java
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileWriterClass> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Content to be assigned to a file> >// Custom input just for illustration purposes> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Create a FileWriter object> >// to write in the file> >FileWriter fWriter =>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into file> >// Note: The content taken above inside the> >// string> >fWriter.write(text);> >// Printing the contents of a file> >System.out.println(text);> >// Closing the file writing connection> >fWriter.close();> >// Display message for successful execution of> >// program on the console> >System.out.println(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exception occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Výkon
File is created successfully with the content.>

Metóda 3: Použitie triedy BufferedWriter
Používa sa na písanie textu do prúdu znakového výstupu. Má predvolenú veľkosť vyrovnávacej pamäte, ale je možné priradiť veľkú veľkosť vyrovnávacej pamäte. Je užitočný na písanie znakov, reťazcov a polí. Je lepšie zabaliť túto triedu s akoukoľvek triedou zapisovača na zapisovanie údajov do súboru, ak nie je potrebný žiadny promptný výstup.
Príklad:
Java
mapovanie v strojopise
// Java Program to write into a File> // Using BufferedWriter Class> // Importing java input output libraries> import> java.io.BufferedWriter;> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assigning the file content> >// Note: Custom contents taken as input to> >// illustrate> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter> >BufferedWriter f_writer> >=>new> BufferedWriter(>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>));> >// Step 2: Write text(content) to file> >f_writer.write(text);> >// Step 3: Printing the content inside the file> >// on the terminal/CMD> >System.out.print(text);> >// Step 4: Display message showcasing> >// successful execution of the program> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >// Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object> >f_writer.close();> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception on console> >// using getMessage() method> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Výkon
git add --all
File is created successfully with the content.>

Nasledujúci príklad ukazuje použitie triedy BufferedWriter na zápis do súboru. Vyžaduje si to aj vytvorenie objektu triedy BufferedWriter, ako je FileWriter na zápis obsahu do súboru. Ale táto trieda podporuje veľký obsah na zápis do súboru pomocou veľkej veľkosti vyrovnávacej pamäte.
Metóda 4: Použitie triedy FileOutputStream
Používa sa na zápis nespracovaných dát toku do súboru. Triedy FileWriter a BufferedWriter sa používajú na zapisovanie iba textu do súboru, ale binárne údaje možno zapisovať pomocou triedy FileOutputStream.
Zápis údajov do súboru pomocou triedy FileOutputStream je znázornený v nasledujúcom príklade. Vyžaduje tiež vytvorenie objektu triedy s názvom súboru na zapisovanie údajov do súboru. Tu sa obsah reťazca skonvertuje na bajtové pole, ktoré sa zapíše do súboru pomocou písať () metóda.
Príklad:
Java
Kat timpf
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileOutputStream Class> // Importing java input output classes> import> java.io.FileOutputStream;> import> java.io.IOException;> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assign the file content> >String fileContent =>'Welcome to geeksforgeeks'>;> >FileOutputStream outputStream =>null>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream> >outputStream =>new> FileOutputStream(>'file.txt'>);> >// Step 2: Store byte content from string> >byte>[] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();> >// Step 3: Write into the file> >outputStream.write(strToBytes);> >// Print the success message (Optional)> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle the exception> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display the exception/s> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >// finally keyword is used with in try catch block> >// and this code will always execute whether> >// exception occurred or not> >finally> {> >// Step 4: Close the object> >if> (outputStream !=>null>) {> >// Note: Second try catch block ensures that> >// the file is closed even if an error> >// occurs> >try> {> >// Closing the file connections> >// if no exception has occurred> >outputStream.close();> >}> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display exceptions if occurred> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Výkon
File is created successfully with the content.>
