Enum v C je tiež známy ako enumerovaný typ. Ide o užívateľom definovaný dátový typ, ktorý pozostáva z celočíselných hodnôt a týmto hodnotám poskytuje zmysluplné názvy. Použitie enum v C uľahčuje pochopenie a údržbu programu. Výčet je definovaný pomocou kľúčového slova enum.
Nasleduje spôsob, ako definovať enum v C:
enum flag{integer_const1, integer_const2,.....integter_constN}; Vo vyššie uvedenej deklarácii definujeme enum pomenovaný ako príznak obsahujúci 'N' celočíselné konštanty. Predvolená hodnota integer_const1 je 0, integer_const2 je 1 atď. Môžeme tiež zmeniť predvolenú hodnotu celočíselných konštánt v čase deklarácie.
Napríklad:
enum fruits{mango, apple, strawberry, papaya}; Predvolená hodnota pre mango je 0, jablko je 1, jahoda je 2 a papája je 3. Ak chceme tieto predvolené hodnoty zmeniť, môžeme postupovať takto:
enum fruits{ mango=2, apple=1, strawberry=5, papaya=7, }; Vyčíslená deklarácia typu
Keďže vieme, že v jazyku C potrebujeme deklarovať premennú preddefinovaného typu, ako je int, float, char atď. Podobne môžeme deklarovať premennú používateľsky definovaného typu údajov, ako napríklad enum. Pozrime sa, ako môžeme deklarovať premennú typu enum.
Predpokladajme, že vytvoríme zoznam stavu typu, ako je uvedené nižšie:
enum status{false,true}; Teraz vytvoríme premennú typu status:
enum status s; // creating a variable of the status type.
Vo vyššie uvedenom príkaze sme deklarovali premennú 's' typu status.
Na vytvorenie premennej môžu byť vyššie uvedené dva príkazy napísané ako:
enum status{false,true} s; V tomto prípade bude predvolená hodnota false rovná 0 a hodnota true bude rovná 1.
Vytvorme si jednoduchý program enum.
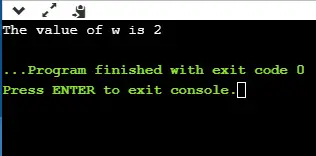
#include enum weekdays{Sunday=1, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday}; int main() { enum weekdays w; // variable declaration of weekdays type w=Monday; // assigning value of Monday to w. printf('The value of w is %d',w); return 0; } Vo vyššie uvedenom kóde vytvoríme typ enum nazvaný ako pracovné dni a obsahuje názov všetkých siedmich dní. Nedeli sme priradili 1 hodnotu a všetky ostatné mená budú mať hodnotu ako predchádzajúca hodnota plus jedna.
Výkon
Ukážme si ďalší príklad, aby sme jasnejšie pochopili enum.
#include enum months{jan=1, feb, march, april, may, june, july, august, september, october, november, december}; int main() { // printing the values of months for(int i=jan;i<=december;i++) { printf('%d, ',i); } return 0; < pre> <p>In the above code, we have created a type of enum named as months which consists of all the names of months. We have assigned a '1' value, and all the other months will be given a value as the previous one plus one. Inside the main() method, we have defined a for loop in which we initialize the 'i' variable by jan, and this loop will iterate till December.</p> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-2.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <h3>Why do we use enum?</h3> <p>The enum is used when we want our variable to have only a set of values. For example, we create a direction variable. As we know that four directions exist (North, South, East, West), so this direction variable will have four possible values. But the variable can hold only one value at a time. If we try to provide some different value to this variable, then it will throw the compilation error.</p> <p>The enum is also used in a switch case statement in which we pass the enum variable in a switch parenthesis. It ensures that the value of the case block should be defined in an enum.</p> <p> <strong>Let's see how we can use an enum in a switch case statement.</strong> </p> <pre> #include enum days{sunday=1, monday, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday, saturday}; int main() { enum days d; d=monday; switch(d) { case sunday: printf('Today is sunday'); break; case monday: printf('Today is monday'); break; case tuesday: printf('Today is tuesday'); break; case wednesday: printf('Today is wednesday'); break; case thursday: printf('Today is thursday'); break; case friday: printf('Today is friday'); break; case saturday: printf('Today is saturday'); break; } return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-3.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <p> <strong>Some important points related to enum</strong> </p> <ul> <li>The enum names available in an enum type can have the same value. Let's look at the example.</li> </ul> <pre> #include int main(void) { enum fruits{mango = 1, strawberry=0, apple=1}; printf('The value of mango is %d', mango); printf('
The value of apple is %d', apple); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-4.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <ul> <li>If we do not provide any value to the enum names, then the compiler will automatically assign the default values to the enum names starting from 0.</li> <li>We can also provide the values to the enum name in any order, and the unassigned names will get the default value as the previous one plus one.</li> <li>The values assigned to the enum names must be integral constant, i.e., it should not be of other types such string, float, etc.</li> <li>All the enum names must be unique in their scope, i.e., if we define two enum having same scope, then these two enums should have different enum names otherwise compiler will throw an error.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Let's understand this scenario through an example.</strong> </p> <pre> #include enum status{success, fail}; enum boolen{fail,pass}; int main(void) { printf('The value of success is %d', success); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-5.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <ul> <li>In enumeration, we can define an enumerated data type without the name also.</li> </ul> <pre> #include enum {success, fail} status; int main(void) { status=success; printf('The value of status is %d', status); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-6.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <h3>Enum vs. Macro in C</h3> <ul> <li>Macro can also be used to define the name constants, but in case of an enum, all the name constants can be grouped together in a single statement. <br> For example, <br> # define pass 0; <br> # define success 1; <br> The above two statements can be written in a single statement by using the enum type. <br> enum status{pass, success};</li> <li>The enum type follows the scope rules while macro does not follow the scope rules.</li> <li>In Enum, if we do not assign the values to the enum names, then the compiler will automatically assign the default value to the enum names. But, in the case of macro, the values need to be explicitly assigned.</li> <li>The type of enum in C is an integer, but the type of macro can be of any type.</li> </ul> <hr></=december;i++)> Výkon

Niektoré dôležité body týkajúce sa enum
- Názvy enum dostupné v type enum môžu mať rovnakú hodnotu. Pozrime sa na príklad.
#include int main(void) { enum fruits{mango = 1, strawberry=0, apple=1}; printf('The value of mango is %d', mango); printf('
The value of apple is %d', apple); return 0; } Výkon

- Ak názvom enum neposkytneme žiadnu hodnotu, kompilátor automaticky priradí predvolené hodnoty názvom enum začínajúcim od 0.
- Môžeme tiež poskytnúť hodnoty názvu enum v ľubovoľnom poradí a nepriradené názvy získajú predvolenú hodnotu ako predchádzajúci plus jeden.
- Hodnoty priradené k názvom enum musia byť integrálne konštantné, t. j. nemali by byť iného typu, ako je reťazec, pohyblivý znak atď.
- Všetky názvy výčtov musia byť jedinečné vo svojom rozsahu, t. j. ak definujeme dve výčty s rovnakým rozsahom, potom by tieto dve výčty mali mať rôzne názvy výčtov, inak kompilátor vyvolá chybu.
Poďme pochopiť tento scenár prostredníctvom príkladu.
#include enum status{success, fail}; enum boolen{fail,pass}; int main(void) { printf('The value of success is %d', success); return 0; } Výkon

- V enumerácii môžeme definovať enumerovaný dátový typ aj bez názvu.
#include enum {success, fail} status; int main(void) { status=success; printf('The value of status is %d', status); return 0; } Výkon

Enum vs. makro v C
- Makro je možné použiť aj na definovanie názvových konštánt, ale v prípade enum môžu byť všetky názvové konštanty zoskupené do jedného príkazu.
Napríklad,
# definovať priechod 0;
# definovať úspech 1;
Vyššie uvedené dva príkazy možno zapísať do jedného príkazu pomocou typu enum.
enum status{pass, success}; - Typ enum sa riadi pravidlami rozsahu, zatiaľ čo makro nedodržiava pravidlá rozsahu.
- Ak v Enum nepriradíme hodnoty k menám enum, potom kompilátor automaticky priradí k názvom enum predvolenú hodnotu. Ale v prípade makra musia byť hodnoty explicitne priradené.
- Typ enum v C je celé číslo, ale typ makra môže byť akéhokoľvek typu.
