Java poskytuje dve veľmi silné knižnice na prácu s údajmi JSON, t.j. JACKSON a Gson knižnice. Často potrebujeme previesť odpovede JSON na mapu, aby sme mohli jednoducho pracovať s vrátenými údajmi JSON.
Údaje JSON môžeme ľahko previesť na mapu, pretože formát JSON je v podstate zoskupením párov kľúč – hodnota a mapa tiež ukladá údaje v pároch kľúč – hodnota.
Poďme pochopiť, ako môžeme použiť knižnice JACKSON aj Gson na konverziu údajov JSON na mapu. Tiež chápeme, ako môžeme použiť obe knižnice na konverziu údajov mapy na JSON.
Predpokladajme, že v systéme máme súbor Sample.json, ktorý obsahuje nasledujúce údaje:
{ 'Name' : 'Donal', 'Mobile' : '89346724', 'Designation' : 'Sr. Salesforce Developer', 'Pet' : 'Dog', 'Address' : 'AMERICA' } JACKSONova knižnica
Aby sme mohli previesť dáta JSON do Java Map, využívame knižnicu JACKSON. Na prácu s knižnicou JACKSON pridávame nasledujúcu závislosť do súboru POM.xml.
com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind 2.5.3
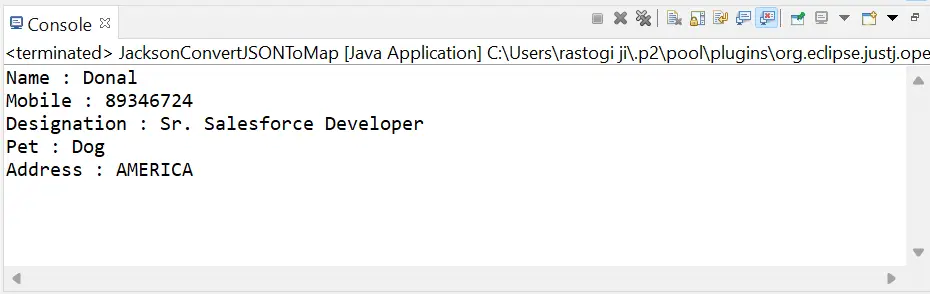
Implementujme logiku prevodu údajov JSON na mapu pomocou tried ObjectMapper, File a TypeReference.
JacksonConvertJSONToMap.java
// import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.io.File; // for reading file data import java.util.Map; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; // create JacksonConvertJSONToMap class to convert JSON data into Java Map public class JacksonConvertJSONToMap { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // create instance of the ObjectMapper class to map JSON data ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // create instance of the File class File fileObj = new File('C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json'); // use try-catch block to convert JSON data into Map try { // read JSON data from file using fileObj and map it using ObjectMapper and TypeReference classes Map userData = mapper.readValue( fileObj, new TypeReference<map>() { }); // print all key-value pairs System.out.println('Name : ' + userData.get('Name')); System.out.println('Mobile : ' + userData.get('Mobile')); System.out.println('Designation : ' + userData.get('Designation')); System.out.println('Pet : ' + userData.get('Pet')); System.out.println('Address : ' + userData.get('Address')); } catch (Exception e) { // show error message e.printStackTrace(); } } } </map> Výkon:
Zoberme si ďalší príklad knižnice Jackson, aby sme pochopili, ako môžeme previesť mapu Java na JSON, pretože často potrebujeme odovzdať mapové dáta do API ako JSON. V tomto príklade teda konvertujeme údaje mapy na JSON a uložíme ich do súboru.
JacksonConvertMapToJson.java
// import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.io.File; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; //create JacksonConvertMapToJSON class to convert Map data into JSON public class JacksonConvertMapToJSON { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // create instance of the ObjectMapper class ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // declare and initialize map (key is of type String and value is of type Object) Map userData = new HashMap(); // declare variables and array to store user entered data String name, price, model; String colors[]; // create an instance of the Scanner class Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // take inputs from the user and store them to the variables System.out.println('Enter the name of the car: '); name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the modal number of the car: '); model = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the price of the car: '); price = sc.nextLine(); colors = new String[3]; colors[0] = 'Red'; colors[1] = 'Black'; colors[2] = 'White'; // close Scanner class object sc.close(); // fill userData map userData.put('Car', name); userData.put('Price', price); userData.put('Model', model); userData.put('Colors', colors); // use try-catch block to convert Java map into JSON try { // use ObjectMapper class to convert Map data into JSON and write it into Sample.json file mapper.writeValue(new File('C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json'), userData); System.out.println('Map data successfully written to the Sample.json file.'); } catch (Exception e) { // handle exception e.printStackTrace(); } } } Výkon:


Knižnica Gson
Gson knižnica je ďalšia knižnica, ktorú môžeme použiť na konverziu údajov JSON na mapu alebo mapových údajov na JSON. Aby sme mohli používať knižnicu Gson, musíme do nášho súboru POM.xml pridať nasledujúcu závislosť.
com.google.code.gson gson 2.8.3
GsonConvertJSONToMap.java
//import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import com.google.gson.Gson; import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; //create GsonConvertJSONToMap class to convert JSON data into Java Map public class GsonConvertJSONToMap { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // create variable loc that store location of the Sample.json file String loc = 'C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json'; String result; try { // read byte data from the Sample.json file and convert it into String result = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(loc))); // store string data into Map by using TypeToken class Map userData = new Gson().fromJson(result, new TypeToken<hashmap>() { }.getType()); // print all key-value pairs System.out.println('Name : ' + userData.get('Name')); System.out.println('Mobile : ' + userData.get('Mobile')); System.out.println('Designation : ' + userData.get('Designation')); System.out.println('Pet : ' + userData.get('Pet')); System.out.println('Address : ' + userData.get('Address')); } catch (IOException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } } } </hashmap> Výkon:

Zoberme si ďalší príklad knižnice Gson, aby sme pochopili, ako previesť mapu Java na JSON. Používanie knižnice Gson je trochu odlišné od knižnice Jackson.
GsonConvertMapToJson.java
//import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import com.google.gson.Gson; //create GsonConvertMapToJson class to convert Map data into JSON public class GsonConvertMapToJson { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // declare and initialize map(key is of type String and value is of type Object) Map userData = new HashMap(); // declare variables and array to store user entered data String name, price, model; String colors[]; // create an instance of the Scanner class Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // take inputs from the user and store them to the variables System.out.println('Enter the name of the car: '); name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the modal number of the car: '); model = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the price of the car: '); price = sc.nextLine(); colors = new String[3]; colors[0] = 'Red'; colors[1] = 'Black'; colors[2] = 'White'; // close Scanner class object sc.close(); // fill userData map userData.put('Car', name); userData.put('Price', price); userData.put('Model', model); userData.put('Colors', colors); // use try-catch block to convert Java map into JSON try (FileWriter file = new FileWriter('C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json')) { // create instance of the Gson Gson gsonObj = new Gson(); // convert userData map to json string String jsonStr = gsonObj.toJson(userData); // use write() of File to write json string into file file.write(jsonStr); // use flush() method to flushes stream file.flush(); System.out.println('Map data successfully written to the Sample.json file.'); } catch (IOException e) { // error handling and exceptions e.printStackTrace(); } } } Výkon:


