Binárny strom je stromová nelineárna dátová štruktúra, ktorá sa používa hlavne na triedenie a vyhľadávanie, pretože ukladá dáta v hierarchickej forme. V tejto časti sa naučíme implementácia binárnej stromovej dátovej štruktúry v Jave . Poskytuje tiež krátky popis štruktúry údajov binárneho stromu.
Binárny strom
Strom, v ktorom má každý uzol (rodič) najviac dve podriadené uzly (ľavý a pravý), sa nazýva binárny strom. Najvyšší uzol sa nazýva koreňový uzol. V binárnom strome uzol obsahuje údaje a ukazovateľ (adresu) ľavého a pravého dcérskeho uzla.
The výška binárneho stromu je počet hrán medzi koreňmi stromu a jeho najvzdialenejší (najhlbší) list. Ak je strom prázdny , výška je 0 . Výška uzla je označená h .
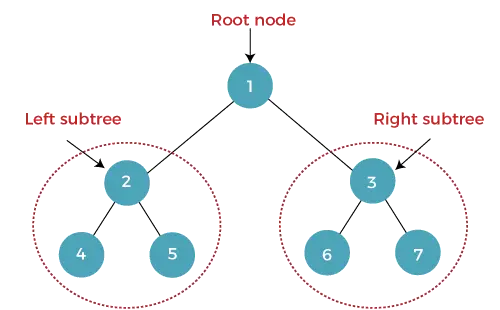
Výška vyššie uvedeného binárneho stromu je 2.
Počet listov a uzlov môžeme vypočítať pomocou nasledujúceho vzorca.
odhlásiť sa z účtu Google v systéme Android
- Maximálny počet listových uzlov je binárny strom: 2h
- Maximálny počet uzlov je binárny strom: 2h+1-1
Kde, h je výška binárneho stromu.
Príklad binárneho stromu

Typy binárnych stromov
V dátovej štruktúre existujú nasledujúce typy binárnych stromov:
- Úplný/prísne binárny strom
- Kompletný binárny strom
- Perfektný binárny strom
- Binárny strom rovnováhy
- Zakorenený binárny strom
- Degenerovaný/patologický binárny strom
- Rozšírený binárny strom
- Šikmý binárny strom
- Doľava skosený binárny strom
- Pravo zošikmený binárny strom
- Závitový binárny strom
- Jednovláknový binárny strom
- Dvojvláknový binárny strom
Implementácia binárneho stromu v Jave
Existuje mnoho spôsobov, ako implementovať binárny strom. V tejto časti budeme implementovať binárny strom pomocou dátovej štruktúry LinkedList. Spolu s tým implementujeme aj príkazy prechodu, vyhľadávanie uzla a vloženie uzla do binárneho stromu.
Implementácia binárneho stromu pomocou LinkedList
Algoritmus
Definujte triedu Node, ktorá obsahuje tri atribúty: dáta vľavo a vpravo. Tu ľavá predstavuje ľavého potomka uzla a pravá predstavuje pravé dieťa uzla.
- Keď sa vytvorí uzol, údaje prejdú do dátového atribútu uzla a ľavý aj pravý sa nastavia na hodnotu null.
- Definujte ďalšiu triedu, ktorá má koreňový atribút.
- Root predstavuje koreňový uzol stromu a inicializuje ho na hodnotu null.
- Skontroluje, či je koreň nulový, čo znamená, že strom je prázdny. Pridá nový uzol ako root.
- V opačnom prípade pridá root do frontu.
- Premenná node predstavuje aktuálny uzol.
- Najprv skontroluje, či má uzol ľavé a pravé dieťa. Ak áno, pridá oba uzly do frontu.
- Ak ľavé dieťa nie je prítomné, pridá sa nový uzol ako ľavé dieťa.
- Ak je prítomný ľavý, pridá nový uzol ako pravé dieťa.
- Prechádza celým stromom, potom vytlačí ľavé dieťa, za ktorým nasleduje koreň a potom pravé dieťa.
BinarySearchTree.java
ak inak v bash shell
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } Výkon:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Operácie binárnych stromov
Na binárnom strome je možné vykonávať nasledujúce operácie:
- Vkladanie
- Vymazanie
- Vyhľadávanie
- Prechádzanie
Java program na vloženie uzla do binárneho stromu
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } Výkon:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Java program na odstránenie uzla v jazyku Java
Algoritmus
- Začnite od koreňa, nájdite najhlbší a najpravejší uzol v binárnom strome a uzol, ktorý chceme vymazať.
- Nahraďte údaje uzla najhlbšieho vpravo uzlom, ktorý sa má odstrániť.
- Potom odstráňte najhlbší uzol úplne vpravo.
Zvážte nasledujúci obrázok.
ktorý vytvoril školu

DeleteNode.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } Výkon:
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
Java program na vyhľadávanie uzla v binárnom strome
Algoritmus
- Definujte triedu Node, ktorá má tri atribúty: dáta vľavo a vpravo. Tu ľavá predstavuje ľavého potomka uzla a pravá predstavuje pravé dieťa uzla.
- Keď sa vytvorí uzol, údaje prejdú do dátového atribútu uzla a ľavý aj pravý sa nastavia na hodnotu null.
- Definujte ďalšiu triedu, ktorá má dva atribúty root a flag.
- Root predstavuje koreňový uzol stromu a inicializuje ho na hodnotu null.
- Príznak sa použije na kontrolu, či sa daný uzol v strome nachádza alebo nie. Spočiatku bude nastavená na hodnotu false.
- Skontroluje, či je koreň nulový, čo znamená, že strom je prázdny.
- Ak strom nie je prázdny, porovná údaje o teplote s hodnotou. Ak sú rovnaké, príznak sa nastaví na hodnotu true a vráti sa.
- Prejdite ľavý podstrom volaním searchNode() rekurzívne a skontrolujte, či je hodnota prítomná v ľavom podstrome.
- Prejdite pravý podstrom rekurzívnym volaním searchNode() a skontrolujte, či je hodnota prítomná v pravom podstrome.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } Výkon:
Element is present in the binary tree.
Prechod binárneho stromu
| Traversal Order | Prvá návšteva | Druhá návšteva | Tretia návšteva |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neporiadok | Navštívte ľavý podstrom v poradí | Navštívte koreňový uzol | Navštívte pravý podstrom v poradí |
| Predobjednať | Navštívte koreňový uzol | Navštívte ľavý podstrom v predobjednávke | Navštívte pravý podstrom v predobjednávke |
| Objednávka poštou | Navštívte ľavý podstrom v postorderi | Navštívte pravý podstrom v postorderi | Navštívte koreňový uzol |
Poznámka: Okrem troch vyššie uvedených prechodov existuje aj ďalšie poradie prechodu, ktoré sa nazýva prechod cez hranice.
Java program na prechod Inorder, Preorder a Postorder Traversal
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } Výkon:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
Okrem vyššie uvedených operácií môžeme vykonávať aj operácie ako veľký uzol, najmenší uzol a súčet všetkých uzlov.
Program Java na nájdenie najväčšieho uzla v binárnom strome
LargestNode.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } Výkon:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
Program Java na nájdenie najmenšieho uzla v binárnom strome
Algoritmus
- Definujte triedu Node, ktorá má tri atribúty: dáta, vľavo a vpravo. Tu ľavá predstavuje ľavého potomka uzla a pravá predstavuje pravé dieťa uzla.
- Keď sa vytvorí uzol, dáta prejdú do dátového atribútu uzla a ľavý aj pravý sa nastavia na hodnotu null.
- Definujte inú triedu, ktorá má atribút root.
Root reprezentovať koreňový uzol stromu a inicializovať ho na hodnotu null.
- Kontroluje, či root je nulový , čo znamená, že strom je prázdny.
- Ak strom nie je prázdny, definujte premennú min, ktorá bude uchovávať údaje o tempe.
- Zistite minimálny uzol v ľavom podstrome rekurzívnym volaním najmenších prvkov(). Uložte túto hodnotu do leftMin. Porovnajte hodnotu min s leftMin a uložte minimálne dve do min.
- Zistite minimálny uzol v pravom podstrome rekurzívnym volaním najmenších prvkov(). Uložte túto hodnotu do rightMin. Porovnajte hodnotu min s rightMin a uložte maximálne dva do min.
- Na konci bude min držať najmenší uzol v binárnom strome.
SmallestNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } Výkon:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
Program Java na nájdenie maximálnej šírky binárneho stromu
Algoritmus
- Definujte triedu Node, ktorá má tri atribúty: dáta vľavo a vpravo. Tu ľavá predstavuje ľavého potomka uzla a pravá predstavuje pravé dieťa uzla.
- Keď sa vytvorí uzol, údaje prejdú do dátového atribútu uzla a ľavý aj pravý sa nastavia na hodnotu null.
- Definujte inú triedu, ktorá má atribút root.
Root predstavuje koreňový uzol stromu a inicializuje ho na hodnotu null.
- Premenná maxWidth uloží maximálny počet uzlov prítomných na akejkoľvek úrovni.
- Front sa používa na prechádzanie binárnym stromom po úrovniach.
- Skontroluje, či je koreň nulový, čo znamená, že strom je prázdny.
- Ak nie, pridajte koreňový uzol do frontu. Premenná nodesInLevel sleduje počet uzlov v každej úrovni.
- Ak nodesInLevel > 0, odstráňte uzol z prednej časti frontu a pridajte jeho ľavý a pravý potomok do frontu. Pri prvej iterácii bude uzol 1 odstránený a jeho dcérske uzly 2 a 3 budú pridané do frontu. V druhej iterácii bude uzol 2 odstránený, jeho deti 4 a 5 budú pridané do fronty atď.
- MaxWidth uloží max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel). Takže v akomkoľvek danom čase bude predstavovať maximálny počet uzlov.
- Toto bude pokračovať, kým sa neprejdú všetky úrovne stromu.
BinaryTree.java
čo je objekt java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } Výkon:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
