The asList() spôsob java.util.Arrays trieda sa používa na vrátenie zoznamu s pevnou veľkosťou podporovaného zadaným poľom. Táto metóda funguje ako a most medzi API založenými na poli a na kolekcii v kombinácii s Collection.toArray(). Vrátený zoznam je serializovateľný a implementuje RandomAccess.
Tip: Toto prebieha v čase O(1).
Syntax:
public static List asList(T... a)>
Parametre: Táto metóda trvá pole a ktorý je potrebné previesť na zoznam. Tu ... je známy ako vararg čo je pole parametrov a funguje podobne ako parameter poľa objektov.
Špeciálna poznámka: Typ poľa musí byť Wrapper Class (Integer, Float atď.) v prípade primitívnych dátových typov (int, float, atď.), t. j. nemôžete zadať int a[], ale môžete zadať Integer a[]. Ak zadáte int a[], táto funkcia vráti zoznam a nie zoznam , pretože v tomto prípade nedochádza k automatickému boxovaniu a int a[] je sám identifikovaný ako objekt a namiesto zoznamu sa vráti pole List of int celých čísel, čo spôsobí chybu v rôznych funkciách kolekcie.
Návratová hodnota: Táto metóda vráti a zobrazenie zoznamu zo zadaného poľa.
Príklad 1:
Java
jpa na jar
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Výkon
programovanie v poli c
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Príklad 2:
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Výkon
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Príklad 3:
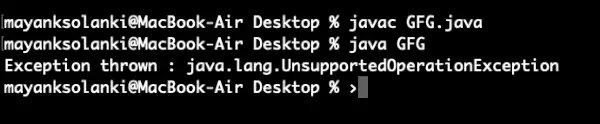
Java
binárny strom vs binárny vyhľadávací strom
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Výkon: