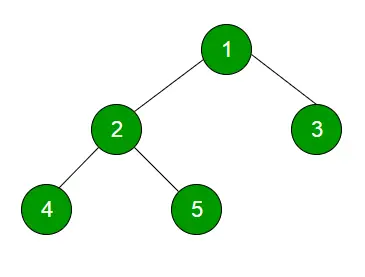
Prechádzanie objednávky úrovne Táto technika je definovaná ako metóda prechodu cez strom tak, že všetky uzly prítomné na rovnakej úrovni sa úplne prejdú pred prechodom na ďalšiu úroveň.
Príklad:
Odporúčaný postup Prechod objednávky na úrovni Vyskúšajte to!Vstup:
Výkon:
1
23
Štyri
Ako funguje Level Order Traversal?
Hlavnou myšlienkou prechodu poradia úrovní je prejsť všetkými uzlami nižšej úrovne pred prechodom na ktorýkoľvek z uzlov vyššej úrovne. To možno vykonať ktorýmkoľvek z nasledujúcich spôsobov:
- ten naivný (nájsť výšku stromu a prejsť cez každú úroveň a vytlačiť uzly tejto úrovne)
- efektívne využívať front.
Level Order Traversal (Naivný prístup):
Nájsť výška stromu. Potom pre každú úroveň spustite rekurzívnu funkciu udržiavaním aktuálnej výšky. Vždy, keď sa úroveň uzla zhoduje, vytlačte tento uzol.
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia vyššie uvedeného prístupu:
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->údajov<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Vypočítajte 'výšku' stromu -- počet // uzlov pozdĺž najdlhšej cesty od koreňového uzla // po najvzdialenejší listový uzol. int vyska(uzol* uzol) { if (uzol == NULL) return 0; else { // Vypočítajte výšku každého podstromu int lheight = height(node->left); int prava = vyska(uzol->vpravo); // Použite väčšiu if (výška> pravá) { return (výška + 1); } else { return (prava + 1); } } } // Pomocná funkcia, ktorá pridelí // nový uzol s danými údajmi a // NULL ľavý a pravý ukazovateľ. node* newNode(int data) { node* Node = new node(); Uzol->údaje = údaje; Uzol->vľavo = NULL; Uzol->vpravo = NULL; návrat (Node); } // Kód ovládača int main() { node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->údaje); else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Vypočítajte 'výšku' stromu -- počet // uzlov pozdĺž najdlhšej cesty od koreňového uzla // po najvzdialenejší listový uzol int height(struct node* node) { if (node == NULL) return 0; else { // Vypočítajte výšku každého podstromu int lheight = height(node->left); int prava = vyska(uzol->vpravo); // Použite väčšiu if (výška> pravá) return (výška + 1); inak návrat (výška + 1); } } // Pomocná funkcia, ktorá pridelí nový uzol // daným údajom a NULL ľavým a pravým ukazovateľom. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); uzol->data = udaje; uzol->vľavo = NULL; uzol->vpravo = NULL; návrat (uzol); } // Program ovládača na testovanie vyššie uvedených funkcií int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); printf('Prechod poradia úrovní binárneho stromu je
'); printLevelOrder(root); návrat 0; }> Java // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>pravý) návrat (výška + 1); inak návrat (výška + 1); } } // Tlač uzlov na aktuálnej úrovni void printCurrentLevel(koreň uzla, int úroveň) { if (root == null) return; if (úroveň == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Program ovládača na testovanie vyššie uvedených funkcií public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); System.out.println('Prechod poradia úrovní' + 'binárny strom je '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # Vypočítajte výšku stromu – počet uzlov # pozdĺž najdlhšej cesty od koreňového uzla nadol po # najvzdialenejší list node def height(node): ak je node None: return 0 else: # Vypočítajte výšku každého podstromu lheight = height(node.left) rheight = height(node.right) # Použite väčšiu, ak lheight> rheight: return lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Program ovládača na testovanie vyššie uvedenej funkcie, ak __name__ == '__main__': root = Uzol(1) root.left = Uzol(2) root.right = Uzol (3) root. left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Prechod poradia úrovne binárneho stromu je -') printLevelOrder(root) # Tento kód prispel Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) { return (výška + 1); } else { return (prava + 1); } } } // Tlač uzlov na aktuálnej úrovni public virtual void printCurrentLevel(koreň uzla, int úroveň) { if (root == null) { return; } if (úroveň == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Kód ovládača public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); Console.WriteLine('Prechod poradia úrovní ' + 'binárneho stromu je '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } } // Tento kód prispel Shrikant13> Javascript // Recursive javascript program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Root of the Binary Tree var root= null; // Function to print level order traversal of tree function printLevelOrder() { var h = height(root); var i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number // of nodes along the longest path // from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. function height(root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree var lheight = height(root.left); var rheight = height(root.right); // Use the larger one if (lheight>pravý) návrat (výška + 1); inak návrat (výška + 1); } } // Tlač uzlov na aktuálnej úrovni funkcia printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (úroveň == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (úroveň> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Program ovládača na testovanie vyššie uvedených funkcií root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); console.log('Prechod poradia úrovní binárneho stromu je '); printLevelOrder(); // Tento kód prispel umadevi9616> Výkon
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Časová zložitosť: O(N), kde N je počet uzlov v šikmom strome.
Pomocný priestor: O(1) Ak sa uvažuje zásobník rekurzie, použitý priestor je O(N).
zoznam java je prázdny
Level Order Traversal pomocou Fronta
Musíme navštíviť uzly na nižšej úrovni pred akýmkoľvek uzlom na vyššej úrovni, táto myšlienka je dosť podobná myšlienke frontu. Posuňte uzly nižšej úrovne vo fronte. Keď je navštívený akýkoľvek uzol, vyberte tento uzol z frontu a zatlačte potomka tohto uzla do frontu.
To zaisťuje, že uzol nižšej úrovne bude navštívený pred akýmkoľvek uzlom vyššej úrovne.
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia vyššie uvedeného prístupu:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // Zaradiť koreň a inicializovať výšku q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Tlač prednej časti frontu a jeho odstránenie z frontu Node* node = q.front(); cout<< node->údajov<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->vľavo != NULL) q.push(uzol->vľavo); // Zaradiť pravého potomka if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // Funkcia pomôcky na vytvorenie nového uzla stromu Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->data = data; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; návratová teplota; } // Program ovládača na testovanie vyššie uvedených funkcií int main() { // Vytvorme binárny strom zobrazený v diagrame vyššie Node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->údaje); // Zaradiť ľavý potomok if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Zaradenie pravého potomka if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Dequeue node a urobte z neho temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Užitočné funkcie struct node** createQueue(int* vpredu, int* vzadu) { struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *predné = *zadné = 0; návratová fronta; } void enQueue(struct node** front, int* zadný, struct node* nový_uzol) { queue[*zadný] = nový_uzol; (*zadné)++; } struct node* deQueue(struct node** front, int* front) { (*front)++; návratový front[*predný - 1]; } // Pomocná funkcia, ktorá alokuje nový uzol s // danými údajmi a NULL ľavým a pravým ukazovateľom. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); uzol->data = udaje; uzol->vľavo = NULL; uzol->vpravo = NULL; návrat (uzol); } // Program ovládača na testovanie vyššie uvedených funkcií int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); printf('Prechod poradia úrovní binárneho stromu je
'); printLevelOrder(root); návrat 0; }> Java // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuefront = nový LinkedList(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() odstráni súčasnú hlavičku. Node tempNode = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Zaradiť ľavého potomka if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // Zaradenie pravého potomka if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Vytvorenie binárneho stromu a zadanie // uzlov BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = new Node(1); tree_level.root.left = new Node(2); tree_level.root.right = new Node(3); tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5); System.out.println('Prechod poradia úrovní binárneho stromu je - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # Vytlačiť prednú časť frontu a # odstrániť ju z frontu print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # Zaradiť ľavý potomok, ak node.left nie je Žiadne: queue.append(node.left) # Zaradiť pravé dieťa, ak node.right nie je Žiadne: queue.append(node.right) # Program ovládača na otestovanie funkcie uvedenej vyššie, ak __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Poradenie úrovne prechodu binárneho stromu je - ') printLevelOrder(root) # Tento kód pridal Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuefront = nový front(); queue.Enqueue(root); while (queue.Count != 0) { Node tempNode = queue.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // Zaradiť ľavého potomka if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Zaradenie pravého potomka if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Kód ovládača public static void Main() { // Vytvorenie binárneho stromu a zadanie // uzlov BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = new Node(1); tree_level.root.left = new Node(2); tree_level.root.right = new Node(3); tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5); Console.WriteLine('Prechod poradia úrovní ' + 'binárneho stromu je - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } } // Tento kód prispel PrinceRaj1992> Javascript class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> Výkon
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Časová zložitosť: O(N), kde N je počet uzlov v binárnom strome.
Pomocný priestor: O(N), kde N je počet uzlov v binárnom strome.