Eulerovská cesta je cesta v grafe, ktorá navštívi každú hranu práve raz. Eulerovský okruh je eulerovská cesta, ktorá začína a končí na rovnakom vrchole.


Ako zistiť, či je daný graf eulerovský alebo nie?
Problém je rovnaký ako v nasledujúcej otázke. Je možné nakresliť daný graf bez toho, aby ste zdvihli ceruzku z papiera a bez toho, aby ste viackrát obkresľovali niektorú z hrán?
Graf sa nazýva eulerovský, ak má eulerovský cyklus, a poloeulerovský, ak má eulerovskú cestu. Zdá sa, že problém je podobný Hamiltonovej ceste, čo je NP úplný problém pre všeobecný graf. Našťastie vieme zistiť, či daný graf má eulerovskú cestu alebo nie v polynomiálnom čase. V skutočnosti ho môžeme nájsť v čase O(V+E).
Nasleduje niekoľko zaujímavých vlastností neorientovaných grafov s eulerovskou dráhou a cyklom. Tieto vlastnosti môžeme použiť na zistenie, či je graf eulerovský alebo nie.
Eulerovský cyklus: Neorientovaný graf má eulerovský cyklus, ak sú splnené dve podmienky.
- Všetky vrcholy s nenulovým stupňom sú spojené. Nestaráme sa o vrcholy s nulovým stupňom, pretože nepatria do Eulerovského cyklu alebo cesty (berieme do úvahy iba všetky hrany).
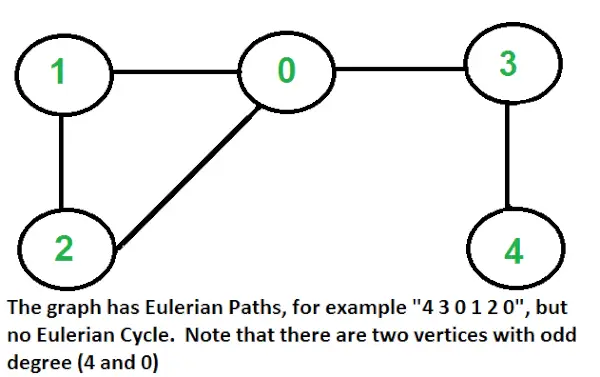
- Všetky vrcholy majú párny stupeň.
Eulerovská cesta: Neorientovaný graf má eulerovskú cestu, ak sú splnené dve podmienky.
- Rovnaké ako podmienka (a) pre Eulerovský cyklus.
- Ak nula alebo dva vrcholy majú nepárny stupeň a všetky ostatné vrcholy majú párny stupeň. Všimnite si, že iba jeden vrchol s nepárnym stupňom nie je možný v neorientovanom grafe (súčet všetkých stupňov je vždy párny v neorientovanom grafe)
Všimnite si, že graf bez hrán sa považuje za eulerovský, pretože neexistujú žiadne hrany, ktoré by sa dali prejsť.
Ako to funguje?
V eulerovskej ceste zakaždým, keď navštívime vrchol v, prechádzame cez dve nenavštívené hrany s jedným koncovým bodom ako v. Preto všetky stredné vrcholy v eulerovskej ceste musia mať párny stupeň. Pre Eulerovský cyklus môže byť akýkoľvek vrchol stredným vrcholom, preto musia mať všetky vrcholy párny stupeň.
Implementácia:
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A class that represents an undirected graph> class> Graph> {> >int> V;>// No. of vertices> >list<>int>>*adj;>// A dynamic array of adjacency lists> public>:> >// Constructor and destructor> >Graph(>int> V) {>this>->V = V; adj =>new> list<>int>>[V]; }> >~Graph() {>delete> [] adj; }>// To avoid memory leak> >// function to add an edge to graph> >void> addEdge(>int> v,>int> w);> >// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not> >int> isEulerian();> >// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >bool> isConnected();> >// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();> >void> DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[]);> };> void> Graph::addEdge(>int> v,>int> w)> {> >adj[v].push_back(w);> >adj[w].push_back(v);>// Note: the graph is undirected> }> void> Graph::DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[])> {> >// Mark the current node as visited and print it> >visited[v] =>true>;> >// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >list<>int>>::iterátor i;> >for> (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)> >if> (!visited[*i])> >DFSUtil(*i, visited);> }> // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected.> // It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> bool> Graph::isConnected()> {> >// Mark all the vertices as not visited> >bool> visited[V];> >int> i;> >for> (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) návrat false; vrátiť true; } /* Funkcia vráti jednu z nasledujúcich hodnôt 0 --> Ak graf nie je eulerovský 1 --> ak má graf Eulerovu cestu (semieulerovský) 2 --> ak má graf Eulerov obvod (eulerovský) */ int Graph::isEulerian() { // Kontrola, či sú všetky vrcholy nenulového stupňa spojené if (isConnected() == false) return 0; // Počítanie vrcholov s nepárnym stupňom int nepárne = 0; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() & 1) nepárne++; // Ak je počet väčší ako 2, potom graf nie je eulerovský, ak (nepárne> 2) vráti 0; // Ak je nepárne počet je 2, potom semi-euleriánsky // Ak je nepárny počet 0, potom eulerovský // Všimnite si, že nepárny počet nemôže byť nikdy 1 pre neorientovaný návrat grafu (nepárny) } // Funkcia na spustenie testovacích prípadov test(Graf &g) { int res = g.isEulerian(); if (res == 0) cout<< 'graph is not Eulerian
'; else if (res == 1) cout << 'graph has a Euler path
'; else cout << 'graph has a Euler cycle
'; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { // Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures Graph g1(5); g1.addEdge(1, 0); g1.addEdge(0, 2); g1.addEdge(2, 1); g1.addEdge(0, 3); g1.addEdge(3, 4); test(g1); Graph g2(5); g2.addEdge(1, 0); g2.addEdge(0, 2); g2.addEdge(2, 1); g2.addEdge(0, 3); g2.addEdge(3, 4); g2.addEdge(4, 0); test(g2); Graph g3(5); g3.addEdge(1, 0); g3.addEdge(0, 2); g3.addEdge(2, 1); g3.addEdge(0, 3); g3.addEdge(3, 4); g3.addEdge(1, 3); test(g3); // Let us create a graph with 3 vertices // connected in the form of cycle Graph g4(3); g4.addEdge(0, 1); g4.addEdge(1, 2); g4.addEdge(2, 0); test(g4); // Let us create a graph with all vertices // with zero degree Graph g5(3); test(g5); return 0; }> |
java zoznamy
>
>
Java
// A Java program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> import> java.io.*;> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.LinkedList;> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> LinkedList adj[];> >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> LinkedList[v];> >for> (>int> i=>0>; i adj[i] = new LinkedList(); } //Function to add an edge into the graph void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].add(w);// Add w to v's list. adj[w].add(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS void DFSUtil(int v,boolean visited[]) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { int n = i.next(); if (!visited[n]) DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from boolean isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited boolean visited[] = new boolean[V]; int i; for (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) návrat false; vrátiť true; } /* Funkcia vráti jednu z nasledujúcich hodnôt 0 --> Ak graf nie je eulerovský 1 --> ak má graf Eulerovu cestu (semieulerovský) 2 --> ak má graf Eulerov obvod (eulerovský) */ int isEulerian() { // Kontrola, či sú všetky vrcholy nenulového stupňa spojené, ak (isConnected() == false) return 0; // Počítanie vrcholov s nepárnym stupňom int nepárne = 0; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size()%2!=0) nepárne++; // Ak je počet väčší ako 2, potom graf nie je eulerovský, ak (nepárne> 2) vráti 0; / / Ak je nepárny počet 2, potom poloeulerovský // Ak je nepárny počet 0, potom eulerovský // Všimnite si, že nepárny počet nemôže byť nikdy 1 pre neorientovaný návrat grafu (nepárny==2) } //; Funkcia na spustenie testovacích prípadov void test() { int res = isEulerian() if (res == 0) System.out.println('graf nie je eulerovský' else if (res == 1) Systém. out.println('graf má Eulerovu cestu' else System.out.println('graf má Eulerov cyklus' } // Metóda ovládača public static void main(String args[]) { /); / Vytvorme a otestujme grafy uvedené na obrázkoch Graph g1 = new Graph(5); g1.addEdge(0, 2); (0, 3). g1.test(); g2.pridaj(1, 2); pridajHranu(2, 1); g2.pridajHranu(3, 4); g2.test(5); .addEdge(1, 0); g3.addEdge(0, 2); g3.addEdge(2, 1); g3.addEdge(0, 3); g3.addEdge(3, 4); g3.addEdge(1, 3); g3.test(); // Vytvorme graf s 3 vrcholmi // spojenými v tvare cyklu Graph g4 = new Graph(3); g4.addEdge(0, 1); g4.addEdge(1, 2); g4.addEdge(2, 0); g4.test(); // Vytvorme graf so všetkými vrcholmi // s nulovým stupňom Graph g5 = new Graph(3); g5.test(); } } // Tento kód prispel Aakash Hasija> |
>
>
Python3
# Python program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #Complexity : O(V+E)> from> collections>import> defaultdict> # This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list representation> class> Graph:> >def> __init__(>self>, vertices):> >self>.V>=> vertices># No. of vertices> >self>.graph>=> defaultdict(>list>)># default dictionary to store graph> ># function to add an edge to graph> >def> addEdge(>self>, u, v):> >self>.graph[u].append(v)> >self>.graph[v].append(u)> ># A function used by isConnected> >def> DFSUtil(>self>, v, visited):> ># Mark the current node as visited> >visited[v]>=> True> ># Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >for> i>in> self>.graph[v]:> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False>:> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> >'''Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are> >connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> >node with non-zero degree'''> >def> isConnected(>self>):> ># Mark all the vertices as not visited> >visited>=> [>False>]>*>(>self>.V)> ># Find a vertex with non-zero degree> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i]) !>=> 0>:> >break> ># If there are no edges in the graph, return true> >if> i>=>=> self>.V>->1>:> >return> True> ># Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False> and> len>(>self>.graph[i])>>0>:> >return> False> >return> True> >'''The function returns one of the following values> >0 -->Ak graf nie je eulerovský> >1 -->Ak má graf Eulerovu cestu (semi-eulerovská)> >2 -->Ak má graf Eulerov obvod (eulerovský) '''> >def> isEulerian(>self>):> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >if> self>.isConnected()>=>=> False>:> >return> 0> >else>:> ># Count vertices with odd degree> >odd>=> 0> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i])>%> 2> !>=> 0>:> >odd>+>=> 1> >'''If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.> >If odd count is 0, then eulerian> >If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian> >Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph'''> >if> odd>=>=> 0>:> >return> 2> >elif> odd>=>=> 2>:> >return> 1> >elif> odd>>2>:> >return> 0> ># Function to run test cases> >def> test(>self>):> >res>=> self>.isEulerian()> >if> res>=>=> 0>:> >print>(>'graph is not Eulerian'>)> >elif> res>=>=> 1>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler path'>)> >else>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler cycle'>)> # Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures> g1>=> Graph(>5>)> g1.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g1.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g1.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g1.test()> g2>=> Graph(>5>)> g2.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g2.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g2.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g2.addEdge(>4>,>0>)> g2.test()> g3>=> Graph(>5>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g3.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g3.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>3>)> g3.test()> # Let us create a graph with 3 vertices> # connected in the form of cycle> g4>=> Graph(>3>)> g4.addEdge(>0>,>1>)> g4.addEdge(>1>,>2>)> g4.addEdge(>2>,>0>)> g4.test()> # Let us create a graph with all vertices> # with zero degree> g5>=> Graph(>3>)> g5.test()> # This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav> |
>
>
C#
// A C# program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> using> System;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> > // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> public> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> > >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> List<>int>>[]adj;> > >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> List<>int>>[v];> >for> (>int> i=0; i adj[i] = new List |
>
abc s číslami
>
Javascript
> // A Javascript program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class Graph> {> >// Constructor> >constructor(v)> >{> >this>.V = v;> >this>.adj =>new> Array(v);> >for> (let i = 0; i this.adj[i] = []; } // Function to add an edge into the graph addEdge(v,w) { this.adj[v].push(w);// Add w to v's list. this.adj[w].push(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS DFSUtil(v,visited) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex for(let i of this.adj[v]) { let n = i; if (!visited[n]) this.DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited let visited = new Array(this.V); let i; for (i = 0; i |
>
>Výkon
graph has a Euler path graph has a Euler cycle graph is not Eulerian graph has a Euler cycle graph has a Euler cycle>
Časová zložitosť: O(V+E)
Priestorová zložitosť: O(V+E)
Ďalšie články:
Eulerovská cesta a okruh pre riadené grafy.
Fleuryho algoritmus na tlač eulerovskej cesty alebo okruhu?
