Eulerova funkcia Totient Φ(n) pre vstup n je počet čísel v {1, 2, 3, …, n-1}, ktoré sú relatívne prvočíslo k n, t.j. čísla, ktorých GCD (najväčší spoločný deliteľ) s n je 1.
Príklady:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) je 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) je 1, ale gcd(2, 2) je 2.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) je 1 a gcd(2, 3) je 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) je 1 a gcd(3, 4) je 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) je 1, gcd(2, 5) je 1,
gcd(3, 5) je 1 a gcd(4, 5) je 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) je 1 a gcd(5, 6) je 1,
Odporúčaný postup Funkcia Euler Totient Vyskúšajte to!
Ako vypočítať Φ(n) pre vstup n?
A jednoduché riešenie je iterovať cez všetky čísla od 1 do n-1 a počítať čísla s gcd s n ako 1. Nižšie je implementácia jednoduchej metódy na výpočet Eulerovej funkcie Totient pre vstupné celé číslo n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Výkon
phi(1) = 1 phi(2) = 1 phi(3) = 2 phi(4) = 2 phi(5) = 4 phi(6) = 2 phi(7) = 6 phi(8) = 4 phi( 9) = 6 phi(10) = 4
Vyššie uvedený kód volá funkciu gcd O(n) krát. Časová zložitosť funkcie gcd je O(h) kde h je počet číslic v menšom počte daných dvoch čísel. Preto horná hranica na časová zložitosť vyššie uvedeného riešenia je O(N^2 log N) [Ako Φ môže byť najviac Log10n číslic vo všetkých číslach od 1 do n]
Pomocný priestor: O (log N)
Nižšie je a Lepšie riešenie . Myšlienka je založená na Eulerovom produktovom vzorci, ktorý uvádza, že hodnota totientových funkcií je pod súčinovými celkových prvočíselných faktorov p z n.
Vzorec v podstate hovorí, že hodnota Φ(n) sa rovná n vynásobenému vedľajšiemu produktu (1 – 1/p) pre všetky prvočiniteľa p z n. Napríklad hodnota Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Všetky hlavné faktory môžeme nájsť pomocou myšlienky použitej v toto príspevok.
robiť počas java
1) Inicializujte: výsledok = n
2) Spustite cyklus od 'p' = 2 po sqrt(n), vykonajte nasledujúce pre každé 'p'.
a) Ak p delí n, potom
Sada: výsledok = výsledok * (1,0 - (1,0 / (float) p));
Rozdeľte všetky výskyty p v n.
3) Vráťte výsledok
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia vzorca produktu Euler.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; //Keďže v množine {1,2,...,n-1} sú všetky čísla relatívne prvočísla s n //ak n je prvočíslo, vráti (int)výsledok; } // Kód ovládača int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; //Keďže v množine {1,2,...,n-1} sú všetky čísla relatívne prvočísla s n //ak n je prvočíslo, vráti (int)výsledok; } // Program ovládača na testovanie funkcie vyššie int main() { int n; pre (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; //Keďže v množine {1,2,...,n-1} sú všetky čísla relatívne prvočísla s n //ak n je prvočíslo, vráti (int)výsledok; } // Program ovládača na testovanie vyššie uvedenej funkcie public static void main(String args[]) { int n; pre (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : výsledok -= výsledok // n #Keďže v množine {1,2,...,n-1} sú všetky čísla relatívne prvočísla s n #ak n je prvočíslo return int(výsledok) # Driver program na testovanie vyššie uvedenej funkcie pre n v rozsahu (1, 11) : print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Tento kód # prispel Nikita Tiwari.>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; //Keďže v množine {1,2,...,n-1} sú všetky čísla relatívne prvočísla s n //ak n je prvočíslo, vráti (int)výsledok; } // Kód ovládača public static void Main() { int n; pre (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; //Keďže v množine {1,2,...,n-1} sú všetky čísla relatívne prvočísla s n //ak n je prvočíslo return parseInt(result); } // Kód ovládača pre (nech n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $výsledok -= $výsledok / $n; //Keďže v množine {1,2,...,n-1} sú všetky čísla relatívne prvočísla s n //ak n je prvočíslo return intval($result); } // Kód ovládača pre ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> Výkon
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Časová zložitosť: O(Φ n log n)
Pomocný priestor: O(1)
Vo vyššie uvedenej metóde sa môžeme vyhnúť výpočtom s pohyblivou rádovou čiarkou. Myšlienkou je spočítať všetky prvočísla a ich násobky a odpočítať tento počet od n, aby sme získali hodnotu funkcie totient (hlavné faktory a násobky prvočíselných faktorov nebudú mať gcd ako 1)
1) Inicializujte výsledok ako n
2) Uvažujme každé číslo „p“ (kde „p“ sa mení od 2 do Φ(n)).
Ak p delí n, postupujte takto
a) Odčítajte všetky násobky p od 1 do n [všetky násobky p
bude mať gcd viac ako 1 (aspoň p) s n]
b) Aktualizujte n opakovaným delením p.
3) Ak je redukované n väčšie ako 1, odstráňte všetky násobky
z n z výsledku.
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia vyššie uvedeného algoritmu.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; vrátiť výsledok; } // Kód ovládača int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; vrátiť výsledok; } // Program ovládača na testovanie funkcie vyššie int main() { int n; pre (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; vrátiť výsledok; } // Kód ovládača public static void main (String[] args) { int n; pre (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): vysledok -= int(vysledok / n); vrátiť výsledok; # Kód ovládača pre n v rozsahu (1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Tento kód je pridaný # od mits>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= vysledok / n; vrátiť výsledok; } // Kód ovládača static public void Main () { int n; pre (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) vysledok -= parseInt(vysledok / n); vrátiť výsledok; } // Kód ovládača pre (nech n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $vysledok -= (int)$vysledok / $n; návrat $výsledok; } // Kód ovládača pre ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>> Výkon
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Časová zložitosť: O(Φ n log n)
Pomocný priestor: O(1)
Zoberme si príklad na pochopenie vyššie uvedeného algoritmu.
n = 10.
Inicializácia: výsledok = 10
2 je prvočíslo, takže n = n/i = 5, výsledok = 5
3 nie je hlavným faktorom.
Cyklus for sa zastaví po 3, pretože 4*4 nie je menšie alebo rovné
do 10.
Po slučke for je výsledok = 5, n = 5
Keďže n> 1, výsledok = výsledok - výsledok/n = 4
Niektoré zaujímavé vlastnosti Eulerovej funkcie Totient
1) Pre prvočíslo p ,
dôkaz:
Príklady:
2) Pre dve prvočísla a a b
dôkaz:
Príklady:
3) Pre prvočíslo p ,
dôkaz:
Príklady:
4) Pre dve čísla a a b
Špeciálny prípad: gcd(a, b) = 1
Príklady:
Špeciálny prípad :
5) Súčet hodnôt totientných funkcií všetkých deliteľov n sa rovná n.
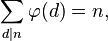
Príklady:
n = 6
faktory = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
6) Najznámejšia a najdôležitejšia vlastnosť je vyjadrená v Eulerova veta :
Veta hovorí, že ak n a a sú koprimé
(alebo relatívne prvočíslo) kladné celé čísla
aΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
The kryptosystém RSA je založená na tejto vete:
V konkrétnom prípade, keď je m prvočíslo, povedzme p, sa Eulerova veta zmení na tzv Fermatova malá veta :
ap-1Φ 1 (proti p)
7) Počet generátorov konečnej cyklickej skupiny pri sčítaní modulo n je Φ(n) .
Súvisiaci článok:
Eulerova funkcia Totient pre všetky čísla menšie alebo rovné n
Optimalizovaná funkcia Euler Totient pre viacnásobné hodnotenia
Referencie:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
git príkazy pre push
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
