Tento tutoriál sa naučí, ako môžeme použiť binárny vyhľadávací algoritmus pomocou Pythonu na nájdenie pozície indexu prvku v danom zozname.
Úvod
Binárne vyhľadávanie je algoritmus na nájdenie konkrétneho prvku v zozname. Predpokladajme, že máme zoznam tisíc prvkov a potrebujeme získať pozíciu indexu konkrétneho prvku. Pomocou binárneho vyhľadávacieho algoritmu môžeme veľmi rýchlo nájsť indexovú pozíciu prvku.
Existuje mnoho vyhľadávacích algoritmov, ale medzi nimi je najobľúbenejšie binárne vyhľadávanie.
Prvky v zozname musia byť zoradené, aby sa použil binárny algoritmus vyhľadávania. Ak prvky nie sú zoradené, najskôr ich zoraďte.
Poďme pochopiť koncept binárneho vyhľadávania.
Koncept binárneho vyhľadávania
V binárnom vyhľadávacom algoritme môžeme nájsť polohu prvku pomocou nasledujúcich metód.
- Rekurzívna metóda
- Iteračná metóda
Po technike prístupu rozdeľ a panuj nasleduje rekurzívna metóda. Pri tejto metóde sa funkcia znova a znova volá, kým nenájde prvok v zozname.
Fibonacciho sekvencia java
Sada príkazov sa niekoľkokrát opakuje, aby sa našla poloha indexu prvku v iteračnej metóde. The zatiaľ čo Na splnenie tejto úlohy sa používa slučka.
Binárne vyhľadávanie je efektívnejšie ako lineárne vyhľadávanie, pretože nepotrebujeme prehľadávať každý index zoznamu. Zoznam musí byť zoradený, aby sa dosiahol binárny algoritmus vyhľadávania.
Poďme krok za krokom implementovať binárne vyhľadávanie.
Máme zoradený zoznam prvkov a hľadáme pozíciu indexu 45.
[12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54]
V našom zozname teda nastavujeme dva ukazovatele. Jeden ukazovateľ sa používa na označenie menšej hodnoty nízka a druhý ukazovateľ sa používa na označenie najvyššej hodnoty vysoká .
Ďalej vypočítame hodnotu stred prvok v poli.
mid = (low+high)/2 Here, the low is 0 and the high is 7. mid = (0+7)/2 mid = 3 (Integer)
Teraz porovnáme hľadaný prvok so strednou hodnotou indexu. V tomto prípade, 32 sa nerovná Štyri. Preto musíme vykonať ďalšie porovnanie, aby sme našli prvok.
Ak sa číslo, ktoré hľadáme, rovná stredu. Potom sa vráťte stred inak prejdite na ďalšie porovnanie.
Číslo, ktoré sa má vyhľadať, je väčšie ako stred číslo, porovnávame n so stredným prvkom prvkov na pravej strane stred a nastavte nízku hodnotu nízka = stredná + 1.
V opačnom prípade porovnajte n s stredný prvok prvkov na ľavej strane stred a nastaviť vysoká do vysoká = stredná - 1.
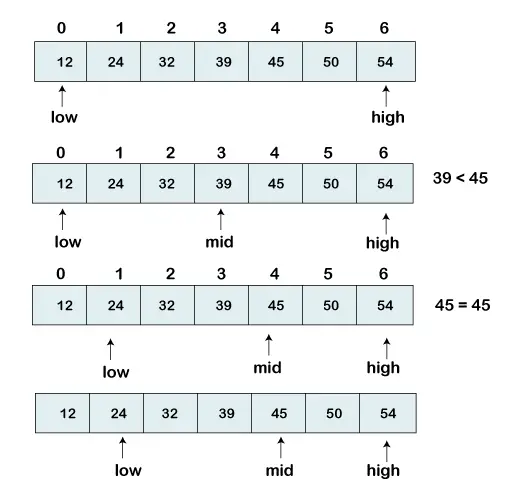
Opakujte, kým nenájdeme číslo, ktoré hľadáme.
Implementujte binárne vyhľadávanie v Pythone
Najprv implementujeme binárne vyhľadávanie iteračnou metódou. Zopakujeme sadu príkazov a zopakujeme každú položku zoznamu. Strednú hodnotu nájdeme, kým sa vyhľadávanie nedokončí.
Poďme pochopiť nasledujúci program iteračnej metódy.
čo je desktop ini
Implementácia Pythonu
# Iterative Binary Search Function method Python Implementation # It returns index of n in given list1 if present, # else returns -1 def binary_search(list1, n): low = 0 high = len(list1) - 1 mid = 0 while low <= 1 2 high: # for get integer result mid="(high" + low) check if n is present at list1[mid] n: high="mid" - smaller, compared to the left of else: return element was not in list, -1 initial list1 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] function call n) !="-1:" print('element index', str(result)) list1') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above program -</p> <ul> <li>We have created a function called <strong>binary_search()</strong> function which takes two arguments - a list to sorted and a number to be searched.</li> <li>We have declared two variables to store the lowest and highest values in the list. The low is assigned initial value to 0, <strong>high</strong> to <strong>len(list1)</strong> - 1 and mid as 0.</li> <li>Next, we have declared the <strong>while</strong> loop with the condition that the <strong>lowest</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>highest</strong> The while loop will iterate if the number has not been found yet.</li> <li>In the while loop, we find the mid value and compare the index value to the number we are searching for.</li> <li>If the value of the mid-index is smaller than <strong>n</strong> , we increase the mid value by 1 and assign it to The search moves to the left side.</li> <li>Otherwise, decrease the mid value and assign it to the <strong>high</strong> . The search moves to the right side.</li> <li>If the n is equal to the mid value then return <strong>mid</strong> .</li> <li>This will happen until the <strong>low</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>high</strong> .</li> <li>If we reach at the end of the function, then the element is not present in the list. We return -1 to the calling function.</li> </ul> <p>Let's understand the recursive method of binary search.</p> <h2>Recursive Binary Search</h2> <p>The recursion method can be used in the binary search. In this, we will define a recursive function that keeps calling itself until it meets the condition.</p> <p>Let's understand the above program using the recursive function.</p> <h3>Python Program</h3> <pre> # Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 2 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> </p> <p>The above program is similar to the previous program. We declared a recursive function and its base condition. The condition is the lowest value is smaller or equal to the highest value.</p> <ul> <li>We calculate the middle number as in the last program.</li> <li>We have used the <strong>if</strong> statement to proceed with the binary search.</li> <li>If the middle value equal to the number that we are looking for, the middle value is returned.</li> <li>If the middle value is less than the value, we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and increase the mid value by one and assign to low.</li> <li>If the middle value is greater than the value we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and decrease the mid value by one and assign it to low.</li> </ul> <p>In the last part, we have written our main program. It is the same as the previous program, but the only difference is that we have passed two parameters in the <strong>binary_search()</strong> function.</p> <p>This is because we can't assign the initial values to the low, high and mid in the recursive function. Every time the recursive is called the value will be reset for those variables. That will give the wrong result.</p> <h2>Complexity</h2> <p>The complexity of the binary search algorithm is <strong>O(1)</strong> for the best case. This happen if the element that element we are looking find in the first comparison. The <strong>O(logn)</strong> is the worst and the average case complexity of the binary search. This depends upon the number of searches are conducted to find the element that we are looking for.</p> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>A binary search algorithm is the most efficient and fast way to search an element in the list. It skips the unnecessary comparison. As the name suggests, the search is divided into two parts. It focuses on the side of list, which is close to the number that we are searching.</p> <p>We have discussed both methods to find the index position of the given number.</p> <hr></=> Vysvetlenie:
Vo vyššie uvedenom programe -
- Vytvorili sme funkciu tzv binárne_vyhľadávanie() funkcia, ktorá má dva argumenty – zoznam na triedenie a číslo, ktoré sa má vyhľadávať.
- Deklarovali sme dve premenné na uloženie najnižšej a najvyššej hodnoty v zozname. Low je priradená počiatočná hodnota 0, vysoká do len(zoznam1) - 1 a stred ako 0.
- Ďalej sme vyhlásili zatiaľ čo slučka s podmienkou, že najnižšie je rovnaký a menší ako najvyššie Cyklus while sa bude opakovať, ak číslo ešte nebolo nájdené.
- V cyklu while nájdeme strednú hodnotu a porovnáme hodnotu indexu s číslom, ktoré hľadáme.
- Ak je hodnota stredného indexu menšia ako n , zvýšime strednú hodnotu o 1 a priradíme ju k Hľadanie sa presunie na ľavú stranu.
- V opačnom prípade znížte strednú hodnotu a priraďte ju k vysoká . Vyhľadávanie sa presunie na pravú stranu.
- Ak sa n rovná strednej hodnote, potom sa vráťte stred .
- Toto sa bude diať až do nízka je rovnaký a menší ako vysoká .
- Ak sa dostaneme na koniec funkcie, prvok sa v zozname nenachádza. Volajúcej funkcii vrátime -1.
Poďme pochopiť rekurzívnu metódu binárneho vyhľadávania.
Rekurzívne binárne vyhľadávanie
Pri binárnom vyhľadávaní je možné použiť metódu rekurzie. V tomto budeme definovať rekurzívnu funkciu, ktorá sa sama volá, kým nesplní podmienku.
Poďme pochopiť vyššie uvedený program pomocou rekurzívnej funkcie.
shreya ghoshal
Program Python
# Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1')
Výkon:
Element is present at index 2
Vysvetlenie
Vyššie uvedený program je podobný predchádzajúcemu programu. Deklarovali sme rekurzívnu funkciu a jej základnú podmienku. Podmienkou je, že najnižšia hodnota je menšia alebo rovná najvyššej hodnote.
- Stredné číslo vypočítame ako v poslednom programe.
- Použili sme ak príkaz pokračovať v binárnom vyhľadávaní.
- Ak sa stredná hodnota rovná číslu, ktoré hľadáme, vráti sa stredná hodnota.
- Ak je stredná hodnota menšia ako hodnota, hľadáme našu rekurzívnu funkciu binárne_vyhľadávanie() znova a zvýšte strednú hodnotu o jeden a priraďte k nízkej.
- Ak je stredná hodnota väčšia ako hodnota, ktorú hľadáme, potom naša rekurzívna funkcia binárne_vyhľadávanie() znova a znížte strednú hodnotu o jednu a priraďte ju k nízkej.
V poslednej časti sme napísali náš hlavný program. Je to rovnaké ako v predchádzajúcom programe, ale jediný rozdiel je v tom, že sme odovzdali dva parametre v binárne_vyhľadávanie() funkciu.
Je to preto, že počiatočné hodnoty nemôžeme priradiť k nízkej, vysokej a strednej v rekurzívnej funkcii. Zakaždým, keď sa zavolá rekurzívny, hodnota týchto premenných sa vynuluje. To prinesie nesprávny výsledok.
Zložitosť
Zložitosť binárneho vyhľadávacieho algoritmu je O(1) v najlepšom prípade. Toto sa stane, ak prvok, ktorý hľadáme, nájdeme v prvom porovnaní. The O(logn) je najhoršia a priemerná zložitosť prípadu binárneho vyhľadávania. Závisí to od počtu vyhľadávaní, ktoré sa vykonávajú, aby sme našli prvok, ktorý hľadáme.
Záver
Binárny vyhľadávací algoritmus je najefektívnejší a najrýchlejší spôsob vyhľadávania prvku v zozname. Preskakuje to zbytočné porovnávanie. Ako už názov napovedá, vyhľadávanie je rozdelené na dve časti. Zameriava sa na stranu zoznamu, ktorá je blízko k číslu, ktoré hľadáme.
Diskutovali sme o oboch metódach na nájdenie pozície indexu daného čísla.
